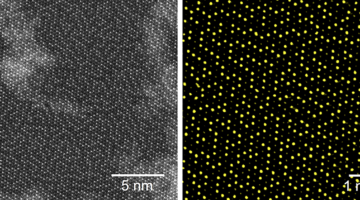
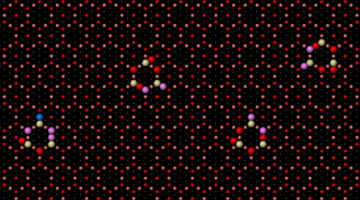
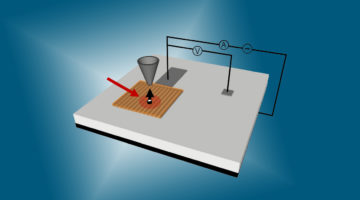
Heterogeneous catalysis is a surface-controlled phenomenon in which different surface sites often show variations in reactivity, posing a major complication for the chemical industry. Here, site-dependent selectivity in oxidation reactions on Pt nanoparticles was identified by conducting IR nanospectroscopy measurements while using allyl-functionalized N-heterocyclic carbenes (allyl-NHCs) as probe molecules. Read more »
ALS Work Using Spectroscopy
These techniques are used to study the energies of particles that are emitted or absorbed by samples that are exposed to the light-source beam and are commonly used to determine the characteristics of chemical bonding and electron motion.
2D Electronics Get an Atomic Tuneup
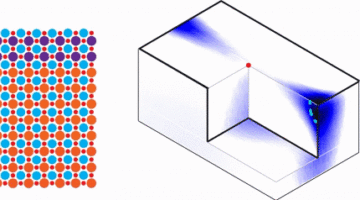
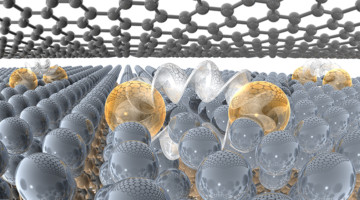
Researchers demonstrated a promising avenue for controlling atomic ordering in semiconductor alloys by engineering frustrated interactions in a 2D transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD). The work could lead to improved semiconductor performance for next-generation electronics such as optoelectronics, thermoelectrics, and sensors. Read more »
Reversible Room-Temperature Fluoride-Ion Insertion in a Tunnel-Structured Transition Metal Oxide Host
Fluoride ions show promise as charge carriers in batteries but have limited cyclability. Here we show the reversible and homogeneous topochemical insertion/deinsertion and bulk diffusion of F ions within the one-dimensional tunnels of submicrometer-sized FeSb2O4 particles at room temperature. Read more »
How Water Promotes Catalysis of Methane to Methanol
Researchers unraveled how water helps catalyze the conversion of methane, the main component of natural gas, into methanol, a liquid fuel. The work supports the efficient production of methanol and other useful chemicals and could help reduce the amount of greenhouse gases released by the flaring and venting of methane. Read more »![]()
![]()
2020 Shirley Award to Honor Miquel Salmeron
By taking surface studies from ultrahigh vacuum to near-ambient pressure, Miquel Salmeron’s work at the ALS has had deep impact on a broad range of scientific questions, revealing the chemical, electronic, and mechanical properties of surfaces and interfaces on the nanometer (and often atomic) scale. Read more »
Scientists Dive Deep Into Hidden World of Quantum States
Researchers discovered two unique electronic properties—a Van Hove singularity and Fermi surface topology—at the interface between atomically thin oxide materials. The results suggest that the system is an ideal platform for investigating how to control superconductivity at the atomic scale in 2D materials. Read more »
Unexpected Rise in Ferroelectricity as Material Thins
Researchers showed that hafnium oxide surprisingly exhibits enhanced ferroelectricity (reversible electric polarization) as it gets thinner. The work shifts the focus of ferroelectric studies from more complex, problematic compounds to a simpler class of materials and opens the door to novel ultrasmall, energy-efficient electronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
The Bottleneck Step of a Complex Catalytic Reaction
The rate-limiting step in catalysis involving oxygen uptake was identified through analysis of the reaction pathways and observations performed under operating conditions. The work lays the foundation for improving the efficiency of energy conversion and storage devices such as fuel cells, catalytic reactors, and batteries. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Scalable Platform for Two-Dimensional Metals
Using a new method for stabilizing a two-dimensional (2D) metal on a large-area platform, researchers probed the origins of the material’s superconductivity. The work represents a notable milestone in advancing 2D materials toward broad applications in topological computing, advanced optics, and molecular sensing. Read more »![]()
![]()
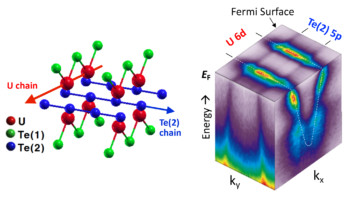
A Forked Path for Superconductivity
Uranium ditelluride (UTe2) exhibits a form of superconductivity that could, in theory, enable fault-tolerant quantum computing. Angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy revealed several aspects of the material’s unusual electronic environment, including one-dimensional conducting channels that are orthogonally oriented. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- …
- 30
- Next Page »