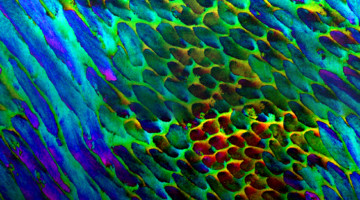
Researchers discovered that, in the nanoscale structure of human enamel (the hard outer layer of teeth), slight crystal misorientations serve as a natural toughening mechanism. The results help explain how human enamel can last a lifetime and provides insight into strategies for designing similarly tough bio-inspired synthetic materials. Read more »![]()
![]()
Machine Learning Helps Stabilize Synchrotron Light
Researchers showed that machine learning can predict noisy fluctuations in the size of beams generated by synchrotron light sources and correct them before they occur. The work solves a decades-old problem and will allow researchers to fully exploit the smaller beams made possible by recent advances in light source technology. Read more »![]()
![]()
Multimodal Study of Ion-Conducting Membranes
Using multiple x-ray characterization tools, researchers showed how chemical and structural changes improve the performance of a novel ion-conducting polymer (ionomer) membrane from 3M Company. The work provides insight into factors impacting the proton conductivity of ionomers used for fuel cells and the production of hydrogen fuel. Read more »![]()
![]()
Infrared Nanospectroscopy at Graphene–Liquid Interfaces
Researchers developed a new infrared approach to probing the first few molecular layers of a liquid in contact with a graphene electrode under operating conditions. The work offers a new way to study the interfaces that are key to understanding batteries, corrosion, and other bio- and electrochemical phenomena. Read more »![]()
![]()
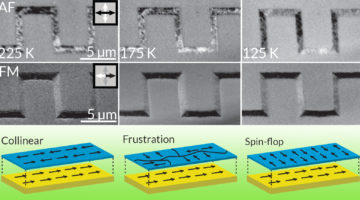
Controlling Spin in Antiferromagnetic Nanostructures
Researchers discovered that the spin configuration of a nanostructured antiferromagnetic material can be affected by the dimensions of features imprinted onto the material. The results suggest that nanoscale patterning can be a viable tool for engineering spin configurations in future antiferromagnetic spintronic devices. Read more »![]()
![]()
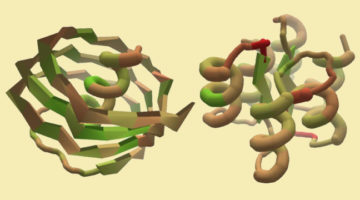
A Citizen-Science Computer Game for Protein Design
Using the computer game, “Foldit,” nonexpert citizen scientists designed new proteins whose structures, verified at the ALS, were equivalent in quality to and more structurally diverse than computer-generated designs. The work shows the potential of using crowd-based creativity in the design of new proteins for fighting illness and disease. Read more »![]()
![]()
Newly Discovered Minerals Reveal Anomalous Origins
Researchers characterized two highly unusual nickel-containing minerals, both unearthed in an ancient geological site in southern central Siberia. The findings extend our understanding of naturally occurring mineral species and varieties and provide useful insights into the environments leading to the formation of potentially valuable mineral ores. Read more »![]()
![]()
Renewed Prospects for Rechargeable Mg Batteries
Contrary to previous reports, it’s possible to create a rechargeable battery using magnesium ions if the electrode material is first conditioned at high temperature. With twice the charge of lithium ions, magnesium ions hold great promise as the basis for high-energy-density batteries suitable for use in electric vehicles. Read more »![]()
![]()
Tuning Material Properties with Laser Light
Researchers demonstrated that coupled electronic and magnetic properties in a material can be repeatably tuned using laser light. The results suggest the possibility of creating microelectronic devices that use a laser beam to erase and rewrite bits of information in materials engineered for random-access memory and data storage. Read more »![]()
![]()
How Light-Harvesting Bacteria Toggle Off and On
Researchers clarified the atomic-level mechanism that enables bacteria to switch light harvesting off and on in response to potentially damaging overexposure to light. The results could have long-range implications for artificial photosynthesis and optogenetics—the use of light to selectively activate biological processes. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- Next Page »