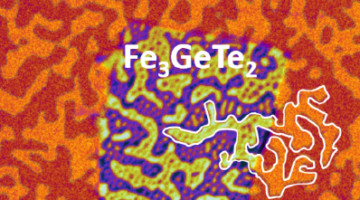
Researchers showed that tiny bubbles of ordered spins (skyrmions) can be induced to form in a material previously considered incompatible with skyrmion formation. The discovery opens up a new class of material systems that exhibit technologically desirable nanoscale features attractive for spintronic applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Science Highlights
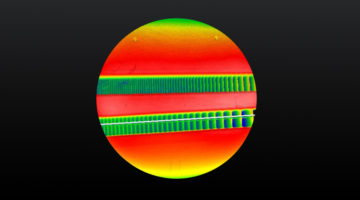
Super-Resolution Measurement of X-Ray Mirrors
ALS researchers, in collaboration with software and nanofabrication small businesses, developed a way to improve the accuracy of instruments that measure the surfaces of x-ray mirrors. The work significantly improves the quality of the data needed for the fabrication and optimal performance of advanced x-ray beamlines and space telescopes. Read more »![]()
![]()
Microstructures Explain Beetle Exoskeleton Strength
Using microtomography and other techniques, researchers identified the exoskeletal toughening mechanisms that explain the crush resistance of the aptly named diabolical ironclad beetle. The observations could be applied in developing tough, impact- and crush-resistant materials for joining dissimilar materials. Read more »![]()
![]()
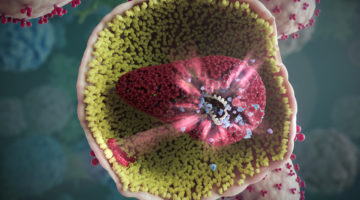
Experimental Drug Targets HIV in a Novel Way
Researchers from Gilead Sciences Inc. solved the structure of an experimental HIV drug bound to a novel target: the capsid protein that forms a shield around the viral RNA. The work could lead to a long-lasting HIV treatment that overcomes the problem of drug resistance and avoids the need for burdensome daily pill-taking. Read more »![]()
![]()
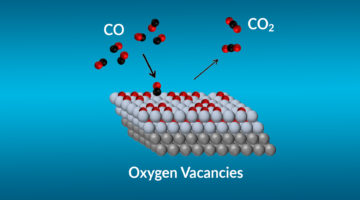
Increasing the Efficiency of CO Catalytic Conversion
Using a combination of tools at the ALS and other facilities, researchers probed specific mechanisms affecting the efficiency of catalysts for CO-to-CO2 conversion. The work brings us closer to the rational design of more effective catalysts for cleaning up toxic CO exhaust and advances our understanding of fundamental catalytic reactions. Read more »![]()
![]()
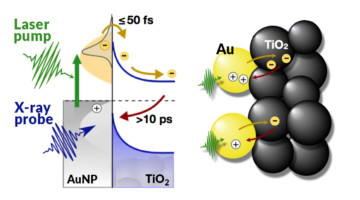
A Probe of Light-Harvesting Efficiency at the Nanoscale
Using time-resolved experiments at the ALS, researchers found a way to count electrons moving back and forth across a model interface for photoelectrochemical cells. The findings provide real-time, nanoscale insight into the efficiency of nanomaterial catalysts that help turn sunlight and water into fuel through artificial photosynthesis. Read more »![]()
![]()
The Flat Band in Magic-Angle Graphene Visualized
Researchers visualized flat band structures associated with exotic electronic phases in stacked graphene layers offset from each other by a “magic angle.” The work corroborates theoretical predictions and has significant implications for phenomena of technological and fundamental interest, such as topological phases and superconductivity. Read more »![]()
![]()
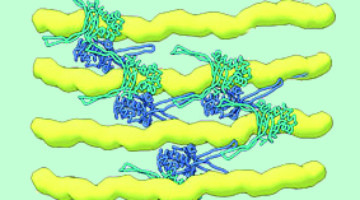
How Proteins Remodel DNA in Bacteria under Stress
Multiscale, multimodal visualization techniques at the ALS enabled researchers to clarify how proteins remodel bacterial DNA in response to stressful environments. The discovery could lead to new strategies for controlling microbial behavior and, eventually, new ways to fight bacterial infections. Read more »![]()
![]()
Toughening Mechanisms in Carp Scales at the Nanoscale
Scientists have characterized carp scales down to the nanoscale, using the ALS to watch how the fibers in the scales react as stress is applied. The resulting insights provide inspiration for the design of advanced synthetic structural materials with unprecedented toughness and penetration resistance. Read more »![]()
![]()
How Water Promotes Catalysis of Methane to Methanol
Researchers unraveled how water helps catalyze the conversion of methane, the main component of natural gas, into methanol, a liquid fuel. The work supports the efficient production of methanol and other useful chemicals and could help reduce the amount of greenhouse gases released by the flaring and venting of methane. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- …
- 27
- Next Page »