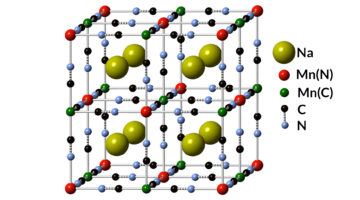
Scientists have detected a novel chemical state of the element manganese that was first proposed about 90 years ago. The discovery enables the design of a high-performance, low-cost battery that, according to its developers, outperforms Department of Energy goals on cost and cycle life for grid-scale energy storage. Read more »![]()
![]()
Science Highlights
Toward Control of Spin States for Molecular Electronics
Researchers demonstrated, via x-ray absorption spectroscopy, that a molecule’s spin state can be reversibly switched at constant room temperature by magnetism. The results represent a major step toward the goal of programmable, nanoscale molecular electronics for high-speed, low-power, logic and memory applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Phase Diagram Leads the Way to Tailored Metamaterial Responses
Researchers discovered an innovative way to independently control two optical responses in a single-material system by utilizing the material’s phase diagram. This unique combination of material, methods, and results could lead to a paradigm shift in the design of metamaterial devices that manipulate light. Read more »![]()
![]()
Tuning the Electronic Structure of a 2D Material
The electronic structure of a stacked 2D material was tuned by in situ electron doping, resulting in a large increase in the splitting of two valence bands. Stacked 2D materials possess an array of tunable properties that are expected to be important for future applications in electronics and optics. Read more »![]()
![]()
Unraveling the Complexities of Auto-Oxidation
Researchers directly observed the formation of highly oxygenated molecules—the elusive products of auto-oxidation reactions relevant to combustion and atmospheric chemistry. A better understanding of auto-oxidation mechanisms could lead to better engines, less air pollution, and improved climate models. Read more »![]()
![]()
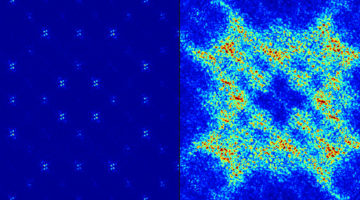
Tuning Magnetic Frustration in a Dipolar Trident Lattice
Researchers designed and fabricated a nanomagnet array in which competing (“frustrated”) magnetic interactions can be directly tuned. Frustrated interactions are key to a wide range of phenomena, from protein folding and magnetic memory to fundamental studies of emergent exotic states. Read more »![]()
![]()
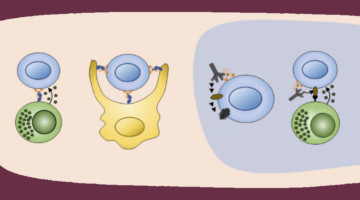
Modified Antibody Clarifies Tumor-Killing Mechanisms
An antibody was modified to activate a specific pathway of the immune system, demonstrating its value in killing tumor cells. The work provides a platform for disentangling different immune-system pathways and could lead to the design of improved immunotherapies. Read more »![]()
![]()
Fuel from the Sun: Insight into Electrode Performance
The mechanisms limiting the performance of hematite electrodes—potentially key components in producing fuel from the sun—have been clarified in interface-specific studies under realistic operating conditions, bringing us a step closer to storing solar energy in chemical fuels. Read more »![]()
![]()
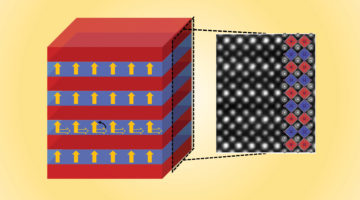
A New Way to Tune Emergent Magnetism
Perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA)—where magnetic moments in a thin film preferentially point out of the plane of the film—is an emergent phenomenon of both fundamental and technological interest. A combination of x-ray techniques demonstrate how to tune PMA in transition-metal oxide multilayers. Read more »![]()
![]()
Coral Exoskeleton Growth Begins Inside Living Tissue
Researchers have discovered some good news regarding corals: the mechanism by which their exoskeletons grow may help them resist the effects of ocean acidification. The discovery, made with PEEM studies, has ramifications not only for the health of coral reefs, but for applications such as 3D printing as well. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- …
- 27
- Next Page »