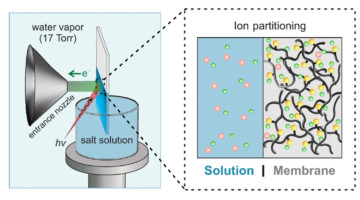
Researchers performed the first direct measurement of the Donnan electrical potential, which arises from an imbalance of charges at membrane-solution interfaces. Considered unmeasurable for over a century, the Donnan potential is relevant to a wide range of fields, from cell biology to energy storage and water desalination. Read more »![]()
![]()
Science Highlights
Watching Nanoparticle Chemistry and Structure Evolve
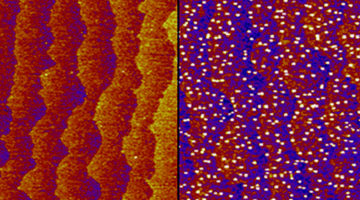
Using a multimodal approach, researchers learned how chemical properties correlate with structural changes during nanoparticle growth. The work will enable a greater understanding of the mechanisms affecting the durability of nanoparticles used to catalyze a broad range of chemical reactions, including clean-energy reactions. Read more »![]()
![]()
Protein Assemblies Show Surprising Variability
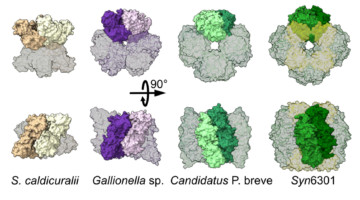
Protein-structure studies performed in part at the ALS helped researchers discover that the protein assemblies in a key carbon-cycling enzyme can rearrange with surprising ease. The findings raise the prospect of genetically tuning the protein in agricultural plant species to produce more productive and resource-efficient crops. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Nano-IR Probe for Proteins in Liquid Environments
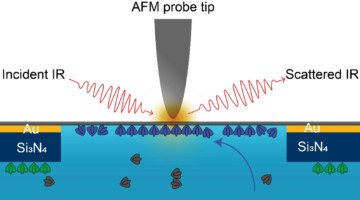
A new technique using infrared (IR) light revealed how the self-assembly of proteins is affected by environmental conditions in a surrounding liquid. This nanoscale probe of soft matter in a liquid matrix will facilitate advances in biology, plastics processing, and energy-relevant applications such as electrocatalysts and batteries. Read more »![]()
![]()
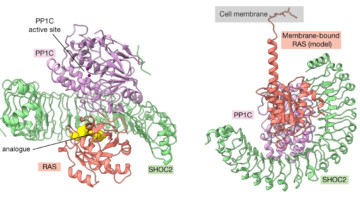
Structures Signal Fresh Targets for Anticancer Drugs
Researchers from Genentech used a suite of methods, including small-angle x-ray scattering, to learn how an assembly of three proteins works together to transmit signals for cell division. The work reveals new targets for the development of drugs that fight certain types of cancer, including lung, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer. Read more »![]()
![]()
Multilayer Stack Opens Door to Low-Power Electronics
Researchers found that a multilayer stack of ultrathin materials exhibits a phenomenon called negative capacitance, which reduces the voltage required for transistor operation. The material is fully compatible with today’s silicon-based technology and is capable of reducing power consumption without sacrificing transistor size or performance. Read more »![]()
![]()
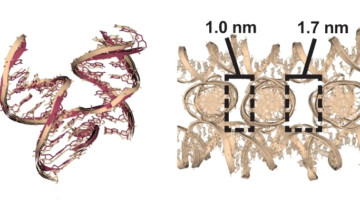
An Expanded Set of DNA Building Blocks for 3D Lattices
Researchers studied 36 DNA-based molecular junctions and discovered factors that yield superior self-assembled 3D lattice structures. The work expands the set of building blocks for lattices that can scaffold molecules into regular arrays, from proteins for structure studies to nanoparticles for nano-antennas and single-particle sensors. Read more »![]()
![]()
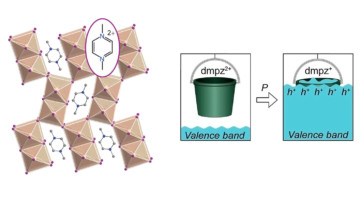
Hybrid Semiconductors Perform Under Pressure
Researchers found that compressing hybrid (organic–inorganic) semiconductors significantly boosts their conductivity. The work demonstrates a novel doping mechanism in which the material’s organic molecules serve as charge reservoirs for tuning charge-carrier concentration, with promising applications in solar cells, lasers, and LEDs. Read more »![]()
![]()
Molecular Switch Triggers Changes in Plant Structure
Using x-ray crystallography, biochemistry, and plant genetics, researchers identified a molecular switch that triggers modifications to plant structure in response to environmental conditions. A greater understanding of this adaptive process will help scientists optimize plants for efficient nutrient uptake and resistance to parasitic species. Read more »![]()
![]()
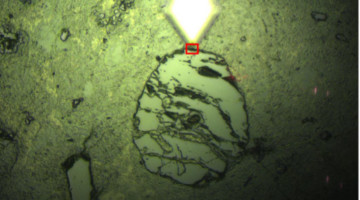
Nanoscale Infrared Study of Meteorite Mineralogy
Using a nanoscale infrared probe, researchers found that the minerals in a meteorite—an artifact representing the solar system’s past—were altered by water on very fine spatial scales. The work sheds light on conditions in the early solar system and lays groundwork for analyzing asteroid samples to be returned to Earth by NASA in 2023. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- …
- 27
- Next Page »