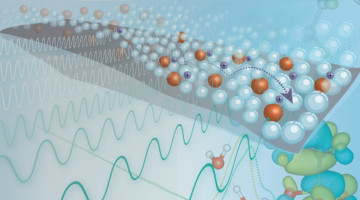
Researchers developed a series of polymer acceptors with controlled backbone regioregularities and side chain structures. All-polymer solar cells based on a RRg-C20 acceptor which has a regioregular backbone and optimal side chain length achieve a high power conversion efficiency of 15.12%, attributed to high electron mobility and optimal blend morphology. Read more »
Label-Free Characterization of Organic Nanocarriers
A technique developed at the ALS enables accurate characterization of organic nanocarriers (molecules that encapsulate other molecules) without the need for disruptive labeling. The method will enable faster, more precise development of exciting new technologies, ranging from targeted drug delivery to oil-spill remediation. Read more »![]()
![]()
High-Efficiency Organic Photovoltaics using Eutectic Acceptor Fibrils to Achieve Current Amplification
Researchers report the fabrication of ternary organic solar cells, achieving a significant JSC boost, by virtue of their optimized crystalline feature, with the formation of eutectic crystalline fibrils. The optimal morphology suppresses energetic disorder and nongeminate recombination, and increases charge transfer and transport, yielding a high efficiency of 17.84% with significant current amplification. Read more »
Additive Lithography–Organic Monolayer Patterning Coupled with an Area-Selective Deposition
This scene depicts the layer-by-layer growth of an inorganic film in a selected area. The alternation of a chemical agent (blue) deposits on a gray substrate to form an inorganic film. A cross-linked organic material (tan) locally inhibits this reaction and prevents film deposition. Furthermore, the pattern-wise cross-linking of this organic film enables nanoscale pattern generation. Read more »
Efficient Organic Solar Cell with 16.88% Efficiency Enabled by Refined Acceptor Crystallization and Morphology with Improved Charge Transfer and Transport Properties
Feng Liu and co‐workers report a detailed structure‐performance relationship to help understand the success of Y6 non‐fullerene acceptors. Through the analysis of the single crystal structure of Y6, it is found that Y6 forms a polymer‐like conjugated backbone through its banana‐shaped structure and π‐π interactions between molecules, and forms a 2D electron transport network under the ordered arrangement of the lattice. Read more »
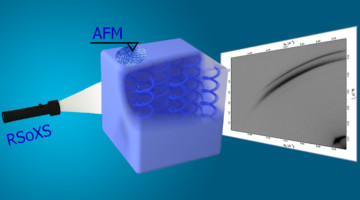
Multimodal Study of Ion-Conducting Membranes
Using multiple x-ray characterization tools, researchers showed how chemical and structural changes improve the performance of a novel ion-conducting polymer (ionomer) membrane from 3M Company. The work provides insight into factors impacting the proton conductivity of ionomers used for fuel cells and the production of hydrogen fuel. Read more »![]()
![]()
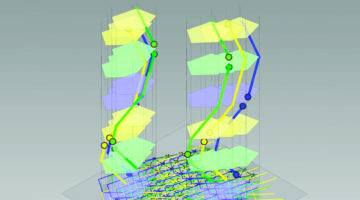
Multiple Levels of Chirality from Achiral Molecules
Liquid crystal samples were found to exhibit up to four levels of chirality, despite being made up of achiral molecules. The work sheds light on how molecular properties and competing interactions “propagate” order from the molecular level up to the microscale, leading to complexity similar to that found in biological materials. Read more »
Chemical and Morphological Origins of Improved Ion Conductivity in Perfluoro Ionene Chain Extended Ionomers
Resonant x-ray scattering and x-ray absorption spectroscopy with elemental sensitivity unravel structural features tied to water–ion domains and discern sulfur-containing groups in sulfonated ionomers, which help delineate chemical factors controlling their phase-separated morphology and governing ion transport. Read more »
Sulfur-linked cyanobiphenyl-based liquid crystal dimers and the twist-bend nematic phase
The synthesis and characterization of cyanobiphenyl-based liquid crystal dimers containing sulfur links between the spacer and mesogenic units are described. Resonant x-ray scattering studies of the twist-bend nematic phase at both the carbon and sulfur absorption edges were performed to determine the critical behaviour of the helical pitch at the transition to the nematic phase. Read more »
Linking Structure to Behavior in Twisted Liquid Crystals
Researchers untangled connections between structure and behavior in a class of liquid crystals consisting of flexible, chain-like molecules that self-organize into twisting patterns. The study opens up new possibilities for designing novel liquid-crystal molecules that allow greater control of nanoscale behavior for technological applications. Read more »![]()
![]()