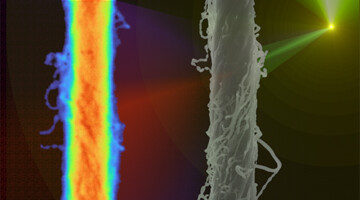
Using the ALS, researchers found quantitative correlations between processing parameters and the structure of ultrafine, polymer-reinforced carbon-nanotube fibers. The work will facilitate the production of high-strength materials, including those needed for positioning target capsules for fusion research at the National Ignition Facility. Read more »![]()
![]()
Insight into How Thermoresponsive Nanomaterials Work
By combining soft x-ray scattering with electron microscopy, researchers learned how nanoscale polymer assemblies in solution restructure in response to heating. The approach can be generalized to many complex, solution-phase, nanoscale processes, and holds promise for driving advances in applications from drug delivery to catalysis. Read more »![]()
![]()
Impact of Thermal Stress on Device Physics and Morphology in Organic Photodetectors
Implementing organic photodetectors (OPDs) into Si-based manufacturing process requires high thermal resistance. This work showcases a comprehensive picture of the impact of high thermal stress (at 200 °C, up to 2 hours) on photosensing performance, bulk and interfacial morphologies, and device physics. Read more »
Extreme Closeup of Copper Electrocatalysts in Action
Researchers at Berkeley Lab have made real-time movies of copper nanoparticles as they evolve to convert carbon dioxide and water into renewable fuels and chemicals. Their new insights could help advance the next generation of solar fuels. Read more »
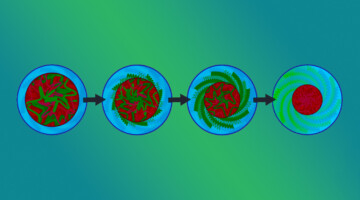
Intrinsically Chiral Twist-Bend Nematogens: Interplay of Molecular and Structural Chirality in the NTB Phase
Cartoon depiction of the formation of the heliconical chiral twist-bend nematic phase (N*TB) from its constituent bent molecules. The presence of a single enantiomer of the chiral, lactate-based liquid crystal dimers biases the formation of helices with only one handedness, unlike in the conventional NTB phase, observed for achiral molecules, for which the left- and right-handed helices are doubly degenerate. Read more »
How a Record-Breaking Copper Catalyst Converts CO2 Into Liquid Fuels
Scientists know that copper has a special ability to transform CO2 into valuable chemicals and fuels. But for many years, they struggled to understand how. Now, a research team has gained new insight by capturing real-time movies of copper nanoparticles as they convert CO2 and water into renewable fuels and chemicals: ethylene, ethanol, and propanol, among others. Read more »
Versatile Sequential Casting Processing for Highly Efficient and Stable Binary Organic Photovoltaics
Ideal bulk heterojunction morphology is critical in organic solar cells (OSCs). Here, researchers show how sequential casting improves device performance in both fullerene- and nonfullerene-based systems, in which the donor and acceptor are deposited sequentially. The film spin-coating method is analogous to the traditional Chinese pancake-making process. Read more »
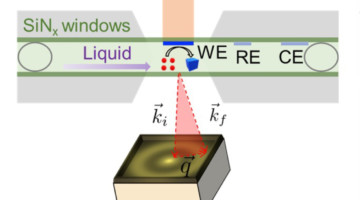
Operando Study of CO2 Reduction by Copper Nanoparticles
Since copper is necessary to catalyze the reduction of CO2, a greenhouse gas, to valuable products, scientists are working hard to improve its selectivity and activity. Now, researchers have developed an operando capability that can help in this effort by simultaneously probing chemical valence and interparticle dynamics. Read more »
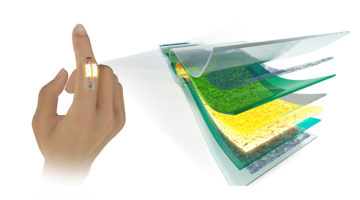
A Brighter Future for Stretchable Electronics
By continuously monitoring physiological signals, wearable “stick-on” sensors not only help people stay healthy, they can also provide early warning of potential health problems. At the ALS, researchers studied the morphology of such a sensor’s active material, which is key to controlling and optimizing its structure and performance. Read more »
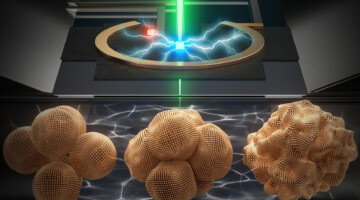
With a Little Help, New Optical Material Assembles Itself
Researchers have demonstrated that tiny concentric nanocircles self-assemble into an optical material with precision and efficiency. Electron microscopy and x-ray scattering revealed the structure and spatial distribution of each ingredient in the resulting materials. The new findings could enable the large-scale manufacturing of multifunctional nanocomposites. Read more »
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- Next Page »