The most expensive component of a battery, the cathode, requires rare transition metals like cobalt. Previous attempts to replace cobalt with inexpensive and non-toxic manganese delivered insufficient performance. Now, researchers have optimized the composition of high-energy-density, high-capacity manganese-based cathodes. Read more »
Graphene-Based Catalyst Improves Peroxide Production
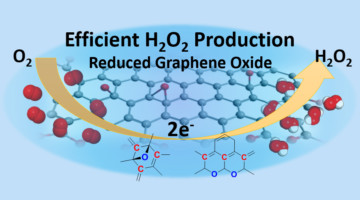
Scientists characterized a graphene-based electrocatalyst that potentially makes the production of hydrogen peroxide more selective, efficient, and cost effective. Hydrogen peroxide is an important commodity chemical with growing demand in many areas, including the electronics industry, wastewater treatment, and paper recycling. Read more »![]()
![]()
New Clues to Oxygen’s Role in Higher-Capacity Batteries
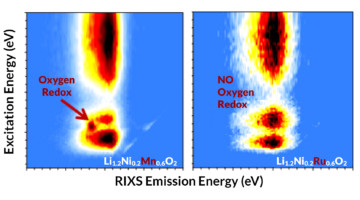
As battery electrodes, layered transition-metal (TM) oxides demonstrate storage capacities far beyond what’s explained solely by TM redox activity. In this work, measurements of the lattice oxygen redox activity in two lithium-rich layered oxides showed strong oxygen redox when manganese was the TM, but not with ruthenium. Read more »
A facile route for the synthesis of heterogeneous crystal structures in hierarchical architectures with vacancy-driven defects via the oriented attachment growth mechanism
TiO2 nanorod arrays based on substrates with heterogeneous crystal structures and remarkable crystalline stability have potential as promising photocatalysts. Researchers synthesized a 1D anatase/rutile heterogeneous TiO2 crystal structure in a hierarchical architecture by forming hybrid organic–inorganic interfaces in a solution-based environment. Read more »
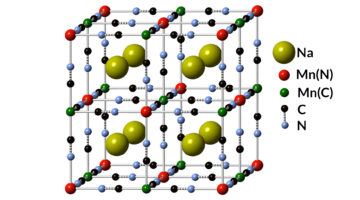
Monovalent Manganese for High-Performance Batteries
Scientists have detected a novel chemical state of the element manganese that was first proposed about 90 years ago. The discovery enables the design of a high-performance, low-cost battery that, according to its developers, outperforms Department of Energy goals on cost and cycle life for grid-scale energy storage. Read more »![]()
![]()
Scientists Confirm Century-Old Speculation on the Chemistry of a High-Performance Battery
Scientists have discovered a novel chemical state of the element manganese. This chemical state, first proposed about 90 years ago, enables a high-performance, low-cost sodium-ion battery that could quickly and efficiently store and distribute energy produced by solar panels and wind turbines across the electrical grid. Read more »
A Path to a Game-Changing Battery Electrode
If you add more lithium to the positive electrode of a lithium-ion battery, it can store much more charge in the same amount of space, theoretically powering an electric car 30 to 50 percent farther between charges. But these lithium-rich cathodes quickly lose voltage, and years of research have not been able to pin down why—until now. Read more »![]()
X-Rays Provide Key Insights on Path to Lithium-Rich Battery Electrode
If you add more lithium to the positive electrode of a lithium-ion battery, it can store much more charge in the same amount of space, theoretically powering an electric car 30 to 50 percent farther between charges. But these lithium-rich cathodes quickly lose voltage, and years of research have not been able to pin down why—until now. Read more »
Elucidating the mechanism of MgB2 initial hydrogenation via a combined experimental–theoretical study
Magnesium borohydride Mg(BH4)2 is a promising solid-state hydrogen-storage material, releasing 14.9 wt% hydrogen upon conversion to MgB2. Although several dehydrogenation pathways have been proposed, the hydrogenation process is less well understood. This study elucidates the key atomistic mechanisms associated with the initial stages of hydrogen uptake within MgB2. Read more »
A Multifunctional Material with Electric-Field Control
Three distinct crystalline phases with different electronic, magnetic, and optical properties were reversibly induced in a material through the insertion and extraction of ions by an electric field at room temperature. Such multifunctional materials are desirable for many applications, from smart windows to spintronics. Read more »![]()
![]()