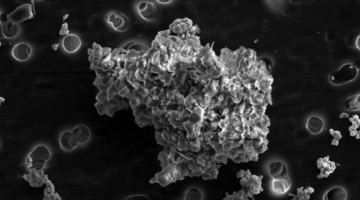
Researchers from Cairo University worked with teams at the ALS to study soil and bone samples dating back 4,000 years. The experiments are casting a new light on Egyptian soil and ancient mummified bone samples that could provide a richer understanding of daily life and environmental conditions thousands of years ago. Read more »
Clues to the Solar System’s Original “Bricks and Mortar”
In comet dust, researchers discovered composite organic-inorganic mineral grains that are likely to be the original “bricks and mortar” of the solar system. “Forensic” samples preserved from the birth of the solar system allow investigations into the nature of the atomic and molecular ancestry of the terrestrial planets and life on Earth. Read more »![]()
![]()
From Moon Rocks to Space Dust: Berkeley Lab’s Extraterrestrial Research
Berkeley Lab has a well-storied expertise in exploring samples of extraterrestrial origin. This research—which has helped us to understand the makeup and origins of objects within and beyond our solar system—stems from long-standing core capabilities in structural and chemical analyses and measurement at the microscale and nanoscale. Read more »
Experiments at Berkeley Lab Help Trace Interstellar Dust Back to Solar System’s Formation
Experiments conducted at the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) helped to confirm that samples of interplanetary particles—collected from Earth’s upper atmosphere and believed to originate from comets—contain dust left over from the initial formation of the solar system. Read more »
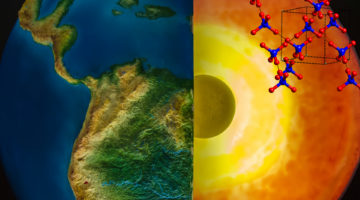
Diamonds From the Deep: Study Suggests Water May Exist in Earth’s Lower Mantle
A new study suggests that water may be more common than expected at extreme depths approaching 400 miles and possibly beyond—within Earth’s lower mantle. The study explored microscopic pockets of a trapped form of crystallized water molecules in a sampling of diamonds from around the world. Read more »
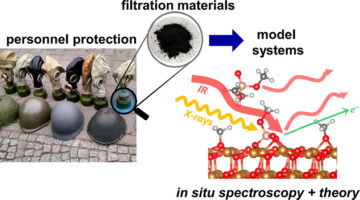
Studying Gas Mask Filters So People Can Breathe Easier
Scientists have put the x-ray spotlight on composite materials in respirators used by the military, police, and first responders. The results provide reassuring news about the effectiveness of current filters and provide fundamental information that could lead to more advanced gas masks as well as protective gear for civilian applications. Read more »
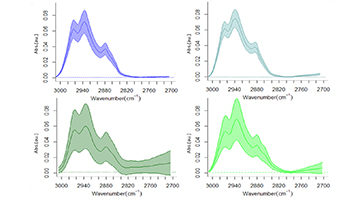
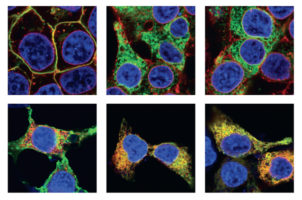
Microbes Linked to Drier Human Skin
Genetic analyses and infrared studies have found that archaea, a type of microbe commonly found in extreme environments, are also found on human skin. The results suggest that an increase in archaea is linked to reduced skin moisture and that they are most abundant in subjects younger than 12 and older than 60. Read more »
Modulating Infrared Light with 2D Black Phosphorus
Two-dimensional materials represent a promising new frontier in the field of optoelectronics. Most progress so far, however, has been in the visible-light range. Now, at the ALS, researchers have measured the infrared transmission spectra of ultrathin samples of black phosphorus under an applied electric field. Read more »![]()
![]()
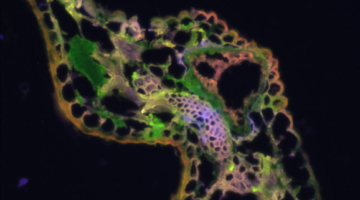
Manganese Reduction-Oxidation Drives Plant Debris Decomposition
ALS research has shown that manganese reduction-oxidation (redox) reactions are an important factor in controlling the rate of plant debris decomposition. Understanding the role of manganese will help build better models to predict how litter decomposition rates—and thus nutrient cycling and the ecosystem carbon balance—may behave in future climate scenarios. Read more »![]()
![]()
New Hope for Retinitis Pigmentosa Patients
Using FTIR microspectroscopy at the NSLS in Brookhaven and at ALS Beamline 1.4.3, scientists got a first glimpse into the structural changes that result from point mutations in opsin, one of the causes of retinitis pigmentosa. Read more »![]()