RNA isn’t just a genetic messenger—it also folds into complex shapes to drive vital biological processes. Scientists are just starting to understand the many functions of these molecules, and how we can harness them for applications in environmental science, agriculture, and medicine. A powerful new RNA structure prediction tool is here to help. Read more »
ALS Work Using Scattering/Diffraction
These techniques make use of the patterns of light produced when x-rays are deflected by the closely spaced lattice of atoms in solids and are commonly used to determine the structures of crystals and large molecules such as proteins.
Building a Gated-Access Fast Lane for Ions
In organic conductors where charge is carried by both electrons and ions, scientists have discovered a way to make the ions move more than ten times faster than in comparable ion-transport methods. The results could apply to a host of areas, including improved battery charging, biosensing, soft robotics, and neuromorphic computing. Read more »
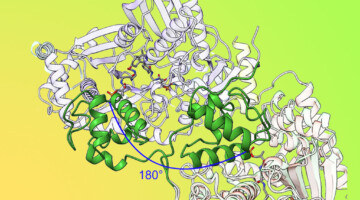
Deep-Dive Inspection of a Molecular Assembly Line
By locking down certain movable parts of a modular drug-building protein, researchers learned new details about how carrier proteins transfer the product protein between modules. The results offer insights that could enable scientists to design and create new and improved medicines, such as antibiotics, using synthetic biology. Read more »![]()
![]()
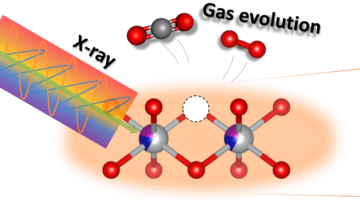
Energy-Saving, Acid-Free, Hard-Rock Lithium Extraction
Researchers used in situ x-ray diffraction to develop a direct, more energy-efficient, and cheaper way to extract lithium from its source mineral, spodumene. The approach not only promises to reduce energy consumption and processing costs but also supports the sustainable scaling of lithium production to meet growing market needs. Read more »![]()
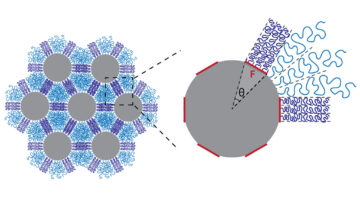
A New Way to Engineer Composite Materials
A new study led by researchers at Berkeley Lab outlines a way to engineer pseudo-bonds in materials. Instead of forming chemical bonds, which is what makes epoxies and other composites so tough, the chains of molecules entangle in a way that is fully reversible. Read more »
Reaction Mechanism of Commercial Lithium-Ion Battery Cathodes
Researchers used soft x-ray resonant inelastic x-ray scattering at the ALS to understand the role of aluminum doping in improving the stability of commercially used cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Read more »
Mind-Blowing Materials: Mimicking Neurons for Faster Computing
Researchers used x-ray absorption spectroscopy and resonant inelastic x-ray scattering at the ALS to uncover the atomic-level mechanism of conductance switching for a neuromorphic material that has the potential for energy-efficient computing. Read more »
Identification of Structurally Novel KRASG12C Inhibitors through Covalent DNA-Encoded Library Screening
DNA-encoded library (DEL) technology was used to prepare a ~1.6 × 107-compound cysteine-reactive library (representative component shown at bottom, cysteine-reactive site indicated). Screening this library against the KRASG12C oncoprotein identified multiple structurally novel inhibitors of this challenging-to-drug target (e.g., frontmost green compound in the X-ray structure at right, covalent bond to KRASG12C indicated). Read more »
Structure of the human autophagy factor EPG5 and the molecular basis of its conserved mode of interaction with Atg8-family proteins
The study reports the first structure of human EPG5 (HsEPG5) determined by cryo-EM and AlphaFold2 modeling. Read more »
Native American Interns Explore Engineering Opportunities at the Lab
This last summer, Berkeley Lab hosted three students from Navajo Technical University in a DOE-funded initiative that partners national labs with learning institutions whose populations are historically underrepresented in science. The goal is to increase enrollment of Native American students in Navajo Tech engineering programs. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- …
- 39
- Next Page »