After decades of tireless science, it was time to spruce up the Beamline 7.3.3 hutch and MAESTRO workspace. Thank you to Leighton Macklin, Shawn Smith, and Mike Lingley for helping us glow up. Now, our outward appearance is as beautiful as the data produced inside. Read more »
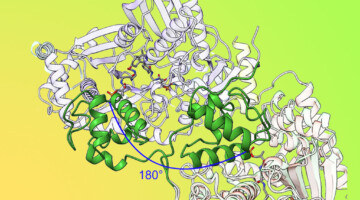
Deep-Dive Inspection of a Molecular Assembly Line
By locking down certain movable parts of a modular drug-building protein, researchers learned new details about how carrier proteins transfer the product protein between modules. The results offer insights that could enable scientists to design and create new and improved medicines, such as antibiotics, using synthetic biology. Read more »![]()
![]()
Protein Pioneer: Enabling Scientists to Design Novel Proteins for the Future
The 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to David Baker, Demis Hassabis, and John M. Jumper for the development of protein structure prediction and design. At the ALS, Baker leveraged high-throughput small-angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) and protein crystallography capabilities to design novel proteins and pave a new pathway for science, technology, and the environment. Read more »
Flat Bands Signal Electrons Trapped in 3D
Researchers found flat electronic band structures—known hallmarks of electrons trapped in two dimensions—but in a material that extends this phenomenon to three dimensions. The work opens up a material framework for exploring superconductivity and other exotic states in three dimensions for advanced electronic applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
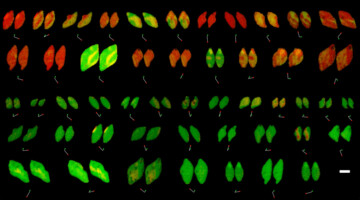
“Computer Vision” Review of X-Ray Movies Leads to New Insights
Using a type of machine learning called “computer vision” to mine data from x-ray movies, researchers made new discoveries about the reactivity of a material in rechargeable batteries. The results suggest that optimizing the carbon layer thickness on the electrode surface could help researchers to design more efficient batteries. Read more »
Will Chueh to Receive the 2023 Shirley Award
Will Chueh of Stanford University is the 2023 winner of the Shirley award for Outstanding Scientific Achievement at the ALS. His selection recognizes Chueh’s deep contributions in operando soft x-ray spectromicroscopy for imaging electrochemical redox phenomena—images and movies for battery and electrocatalytic reactions. Read more »
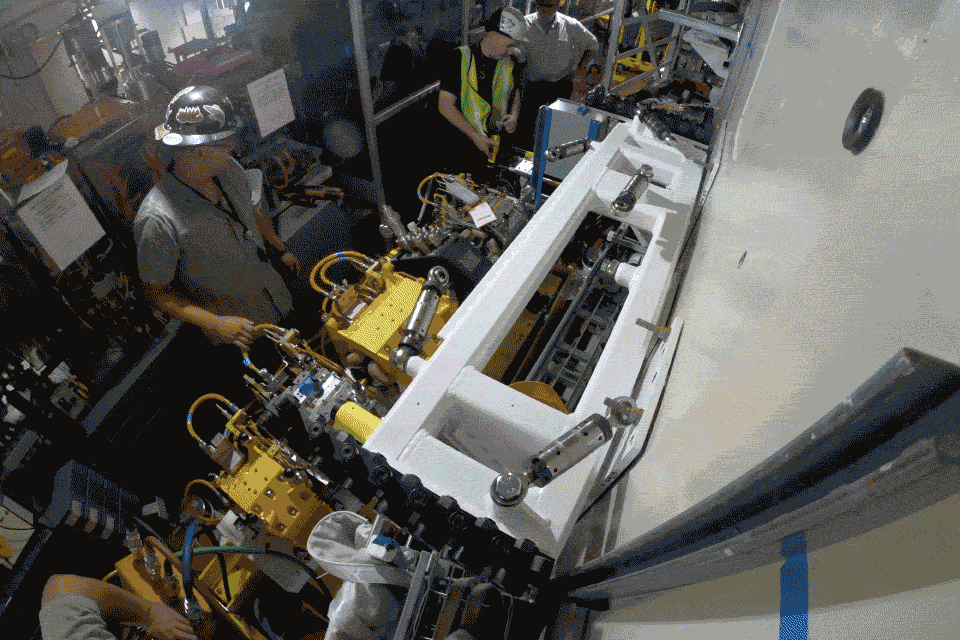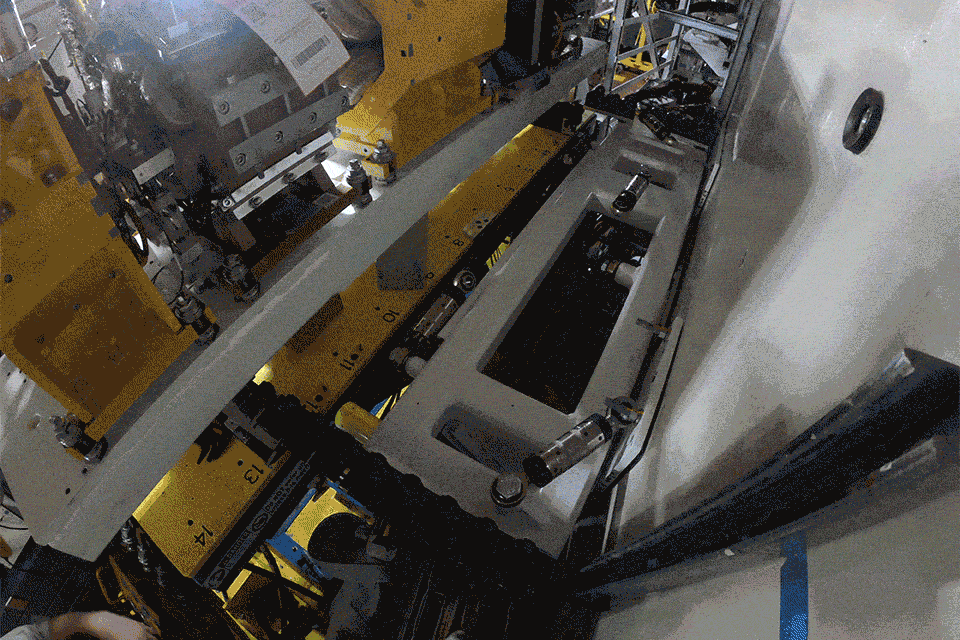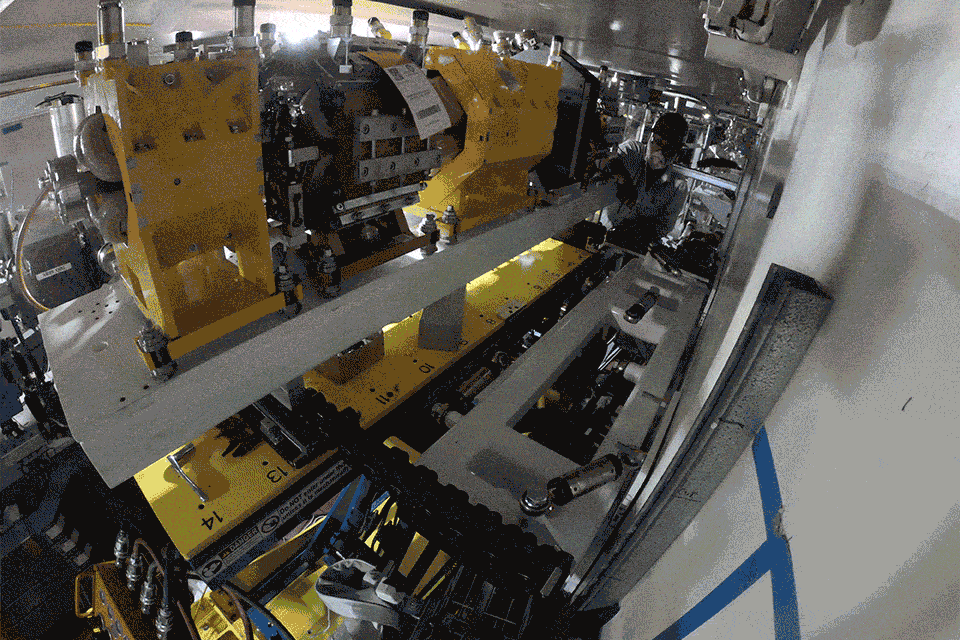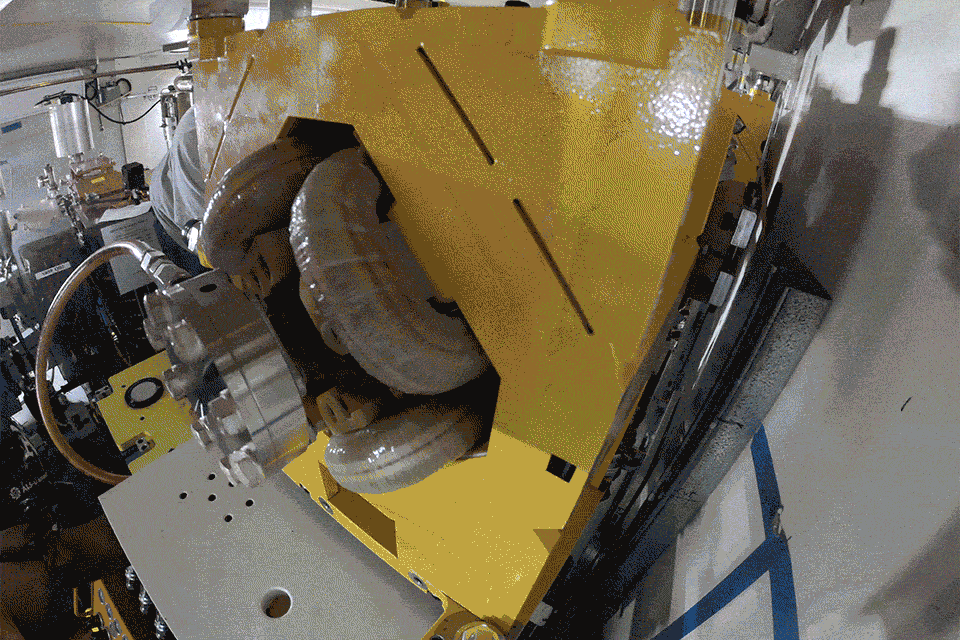
Major ALS-U Milestone: First Accumulator Ring Magnet Rafts Installed
The first magnet rafts of the accumulator ring (AR) have been installed. The AR will work together with the new storage ring to enable on-axis, swap-out injection of electron bunch trains, which is key to achieving ALS-U’s transformational high brightness. The ALS-U project team is installing and commissioning the AR before the one-year dark time that will focus on construction of the new storage ring. More to come about this significant milestone when we recap the summer shutdown!
Chiral Twists and Turns Lead Way to New Materials
Researchers found that, in crystals with structural chirality (left- or right-handedness), tuning the electronic behavior reveals hidden chiral phases and singularities. The results provide a new way to predict, test, and manipulate novel materials that exhibit desirable properties for next-generation electronic and spintronic devices. Read more »![]()
![]()
Nicotine Protonation in Simulated Vaping Aerosols
To better understand how e-cigarette additives alter nicotine chemistry and users’ perceptions of vaping, researchers used x-ray spectroscopy technology at the Advanced Light Source to analyze the acid-base equilibria of additive-enhanced nicotine in simulated vaping aerosols. Read more »
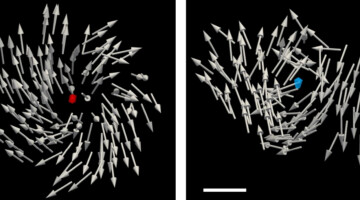
Imaging Topological Magnetic Monopoles in 3D
Researchers created topologically stable magnetic monopoles and imaged them in 3D with unprecedented spatial resolution using a technique developed at the ALS. The work enables the study of magnetic monopole behavior for both fundamental interest and potential use in information storage and transport applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- Next Page »