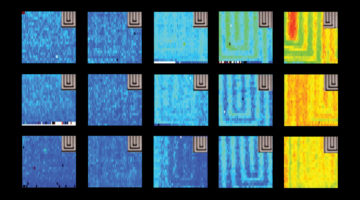
Researchers extracted the relationship between strain and composition in a battery material by applying machine-learning methods to atomic-scale images. The work could lead to more durable batteries and also highlights the potential of integrating microscopy techniques with machine learning to gain insights into complex materials. Read more »![]()
![]()
Industry@ALS
Strategies for Reducing Platinum Waste in Fuel Cells
Industry and university researchers used the ALS to explore why the platinum used as a catalyst in hydrogen fuel cells degrades unevenly. The resulting knowledge has enabled the development of simple, effective strategies to reduce the waste of precious catalyst material, lowering the costs associated with a promising green technology. Read more »![]()
![]()
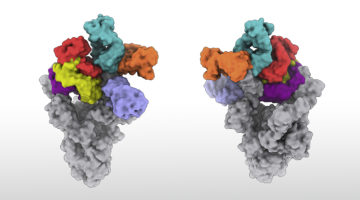
An Antibody That Broadly Neutralizes SARS-CoV-2
An antibody that appears to neutralize all known SARS-CoV-2 strains and closely related coronaviruses was discovered with the help of the ALS. The work highlights principles underlying antibody potency, breadth, and escapability that can guide the development of therapeutics against the current and potential future pandemics. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Two-Dimensional Room-Temperature Magnet
Researchers have made the world’s thinnest (one atom thick) magnet that’s chemically stable under ambient conditions. The two-dimensional material, magnetically characterized at the ALS, could enable big advances in next-generation memory devices, computing, spintronics, and quantum physics. Read more »![]()
![]()
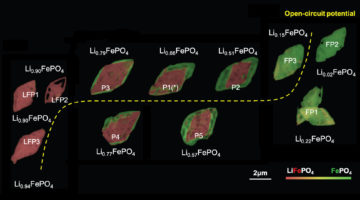
A Multiscale Picture of Oxygen Loss in Battery Electrodes
In lithium-ion batteries, oxygen atoms leak out of electrode particles as the lithium moves back and forth between electrodes. Now, researchers have measured this process at multiple length scales, showing how the oxygen loss changes the electrode’s structure and chemistry, gradually reducing the amount of energy it can store. Read more »
Guiding Target Selection for COVID-19 Antibody Therapeutics
Protein-structure studies helped demonstrate that the primary target of antibody-based COVID-19 immunity is the part of the virus’s spike protein that can most easily mutate. The work anticipated the rise of SARS-CoV-2 variants and guides the selection of antibody therapeutics that are likely to be more resistant to immune escape. Read more »![]()
![]()
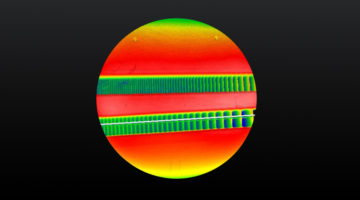
Super-Resolution Measurement of X-Ray Mirrors
ALS researchers, in collaboration with software and nanofabrication small businesses, developed a way to improve the accuracy of instruments that measure the surfaces of x-ray mirrors. The work significantly improves the quality of the data needed for the fabrication and optimal performance of advanced x-ray beamlines and space telescopes. Read more »![]()
![]()
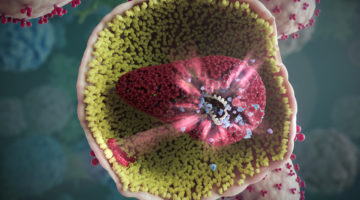
Experimental Drug Targets HIV in a Novel Way
Researchers from Gilead Sciences Inc. solved the structure of an experimental HIV drug bound to a novel target: the capsid protein that forms a shield around the viral RNA. The work could lead to a long-lasting HIV treatment that overcomes the problem of drug resistance and avoids the need for burdensome daily pill-taking. Read more »![]()
![]()
Characterization of EUV Optics using Intrinsic Mask Roughness
Researchers developed an in situ computational technique for measuring aberrations in EUV optics, taking advantage of the surface roughness of photomasks used to transfer circuit patterns onto chips. The technique will prove increasingly valuable in the characterization of coherent light sources and beamline optical systems. Read more »
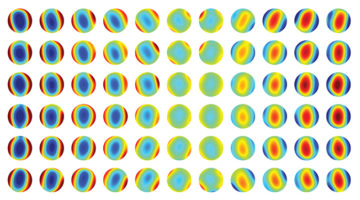
The Flat Band in Magic-Angle Graphene Visualized
Researchers visualized flat band structures associated with exotic electronic phases in stacked graphene layers offset from each other by a “magic angle.” The work corroborates theoretical predictions and has significant implications for phenomena of technological and fundamental interest, such as topological phases and superconductivity. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- …
- 7
- Next Page »