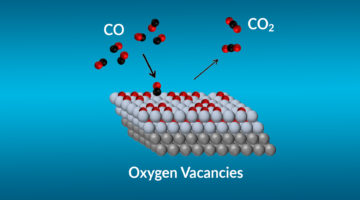
Using a combination of tools at the ALS and other facilities, researchers probed specific mechanisms affecting the efficiency of catalysts for CO-to-CO2 conversion. The work brings us closer to the rational design of more effective catalysts for cleaning up toxic CO exhaust and advances our understanding of fundamental catalytic reactions. Read more »![]()
![]()
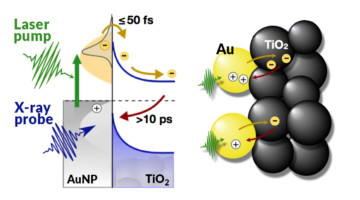
Scientists Capture Candid Snapshots of Electrons Harvesting Light at the Atomic Scale
A team of scientists has gained important new insight into electrons’ role in the harvesting of light in gold/TiO2 nanoparticle photoelectrochemical (PEC) systems. The scientists say that their study can help researchers develop more efficient material combinations for the design of high-performance solar fuels devices. Read more »
A Probe of Light-Harvesting Efficiency at the Nanoscale
Using time-resolved experiments at the ALS, researchers found a way to count electrons moving back and forth across a model interface for photoelectrochemical cells. The findings provide real-time, nanoscale insight into the efficiency of nanomaterial catalysts that help turn sunlight and water into fuel through artificial photosynthesis. Read more »![]()
![]()
2020 Shirley Award to Honor Miquel Salmeron
By taking surface studies from ultrahigh vacuum to near-ambient pressure, Miquel Salmeron’s work at the ALS has had deep impact on a broad range of scientific questions, revealing the chemical, electronic, and mechanical properties of surfaces and interfaces on the nanometer (and often atomic) scale. Read more »
The Bottleneck Step of a Complex Catalytic Reaction
The rate-limiting step in catalysis involving oxygen uptake was identified through analysis of the reaction pathways and observations performed under operating conditions. The work lays the foundation for improving the efficiency of energy conversion and storage devices such as fuel cells, catalytic reactors, and batteries. Read more »![]()
![]()
New Catalyst Resists Destructive Carbon Buildup in Electrodes
Key challenges in the transition to sustainable energy can be met by converting CO2 to CO through the use of solid oxide electrolysis cells. But because these can suffer from carbon deposition at the electrodes, researchers have now identified and tested a new, cerium oxide–based catalyst that is more resistant to carbon buildup. Read more »![]()
Fuel from the Sun: Insight into Electrode Performance
The mechanisms limiting the performance of hematite electrodes—potentially key components in producing fuel from the sun—have been clarified in interface-specific studies under realistic operating conditions, bringing us a step closer to storing solar energy in chemical fuels. Read more »![]()
![]()
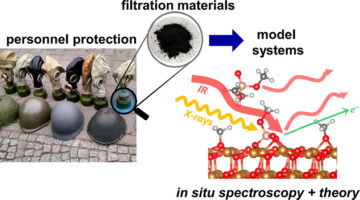
Studying Gas Mask Filters So People Can Breathe Easier
Scientists have put the x-ray spotlight on composite materials in respirators used by the military, police, and first responders. The results provide reassuring news about the effectiveness of current filters and provide fundamental information that could lead to more advanced gas masks as well as protective gear for civilian applications. Read more »
CO Adsorption on Pd(100) Studied by Multimodal Ambient Pressure X-Ray Photoelectron and Infrared Reflection Absorption Spectroscopies
The first combined infrared spectroscopy and ambient-pressure XPS study was demonstrated at Beamline 11.0.2. The in situ vibrational and core-level spectroscopies in the Torr pressure range offer complementary information on the properties of surfaces and adsorbates while closing the pressure gap between laboratory measurements and applications. The multimodal spectroscopy also allowed the identification of the C 1s binding energy and quantification of an uncommon atop CO species on a Pd(100) surface. Read more »
A Closer Look at Dynamic Restructuring in Catalysts
Researchers have structurally and chemically “visualized” the surface of a silver–gold alloy as it reorganizes itself during catalytic activation. The insights gained from this methodology can lead to improved catalysts for energy-intensive industrial applications, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing waste. Read more »![]()
![]()