Scientists have sequenced the genome of a green alga that has drawn commercial interest as a strong producer of quality lipids for biofuel production. The chromosome-assembly genome of Chromochloris zofingiensis provides a blueprint for new discoveries in sustainable biofuels, antioxidants, and other valuable bioproducts. Read more »
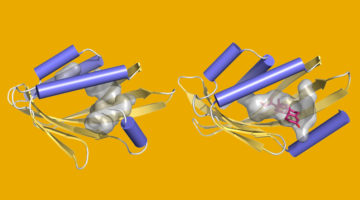
Bending the (β-Sheet) Curve to Shape Protein Cavities
Curved β sheets are basic building blocks of many protein cavities that, by serving as binding sites for other molecules, are essential to protein function. β-sheet curvature can now be controlled with atomic-level accuracy, opening the door to custom-designed sites capable of entirely new functions. Read more »![]()
![]()
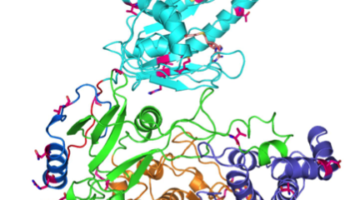
Researchers Gain Insight into Protein Critical to Zika Virus Reproduction
Zika virus is a mosquito-borne infectious disease linked to certain birth defects in infants. Scientists have mapped a key viral protein called NS5, which contains two enzymes: one reduces the body’s ability to mount an immune response against infection and the other helps start the genetic replication process. Read more »
Could This Enzyme Help Turn Biofuel Waste into Something Useful?
A protein used by common soil bacteria is providing new clues in the effort to convert aryl compounds, a common waste product from industrial and agricultural practices, into something of value. This Joint BioEnergy Institute (JBEI) study, which involved ALS Beamline 8.2.2, targets LigM for its role in breaking down aromatic pollutants. Read more »
NCAA Drives Formation of Designed Proteins
A noncanonical amino-acid (NCAA) complex has been found to drive the self-assembly of a computationally designed protein. Bpy-ala, which is “noncanonical” because it’s not among the 20 amino acids that occur naturally, has useful properties that could be used to generate novel photoactive proteins. Read more »
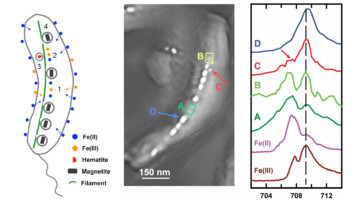
Ptychography of a Bacterium’s Inner Compass
Magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) synthesize chains of magnetic nanocrystals (magnetosomes) that interact with the Earth’s magnetic field like an inner compass needle, simplifying their search for optimum environments. Ptychographic spectra of magnetosomes from a marine MTB provides insight into how these inner compasses form. Read more »
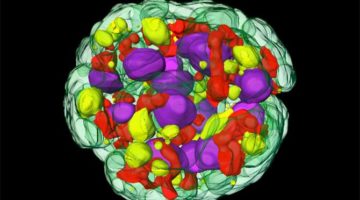
Mapping the Migration of Genetic Material
A powerful soft x-ray microscope captures tomographic images of the genetic material in the nuclei of nerve cells at different stages of maturity. The detailed 3D visualizations show an unexpected connectivity in the genetic material and provide a new understanding of a cell’s evolving architecture. Read more »![]()
![]()
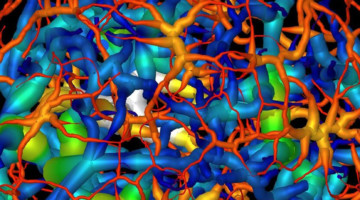
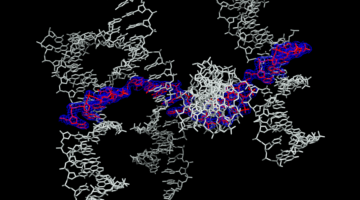
Self-Assembly of a Programmable DNA Lattice
The use of DNA for nanotechnology has gained interest because it is a highly “programmable” polymer with “sticky ends,” allowing the self-assembly of molecular scaffolds for other proteins and molecules. Their high-resolution structures will help map new routes toward the rational design of self-assembling 3D DNA crystals. Read more »
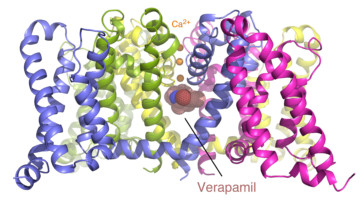
Two Basic Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Drugs
The structures of proteins controlling calcium-ion transport through cell membranes have been revealed, bound to two drugs known as calcium channel blockers. The discovery might accelerate the development of safer and more effective drugs for treating cardiovascular disorders such as high blood pressure, chest pain, and irregular heartbeat. Read more »![]()
![]()
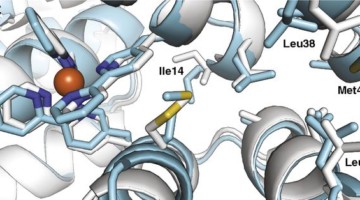
Evolutionary drivers of thermoadaptation in enzyme catalysis
With early life likely to have existed in a hot environment, enzymes had to cope with an inherent drop in catalytic speed caused by lowered temperature. Here, researchers characterize the molecular mechanisms underlying thermoadaptation of enzyme catalysis in adenylate kinase using ancestral sequence reconstruction spanning 3 billion years of evolution. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- …
- 24
- Next Page »