Working as a “molecular sponge,” a bullfrog protein known as saxiphilin provides powerful, yet little understood, protection against deadly neurotoxins produced in red tides. Crystallography studies at the ALS have clarified saxiphilin’s function, potentially enabling better ways to monitor and combat toxins in our oceans and food supplies. Read more »![]()
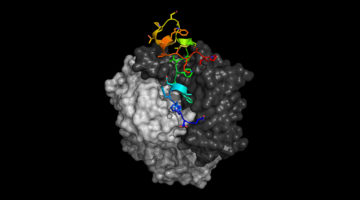
Antibody Uses Mimicry to Block SARS Coronavirus
Protein structures not only revealed how SARS and MERS antibodies inhibit the viruses from attaching to host cells, they also revealed an unprecedented example of receptor mimicry that triggers the cell-invasion machinery of the SARS virus. The results inform efforts to prevent and treat these serious, often deadly, respiratory diseases. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Two-Pronged Defense against Bacterial Self-Intoxication
Researchers solved the structure of a bacterial toxin bound to a neutralizing protein, revealing two distinct mechanisms for how the toxin-producing bacteria avoid poisoning themselves. The findings offer clues to the evolutionary origins of the potent toxins that enable bacterial pathogens to cause human diseases such as cholera and diphtheria. Read more »![]()
![]()
Toward a Blueprint for Anti-influenza Drugs
Researchers obtained high-resolution structures of several influenza antiviral drug molecules bound to their proton-channel targets in both open and closed conformations. The structures provide an atomic-level blueprint from which to design more effective anti-influenza drugs that can overcome growing drug resistance. Read more »![]()
![]()
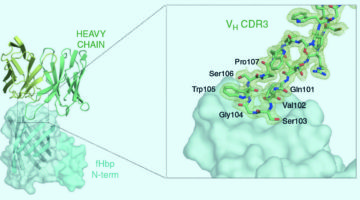
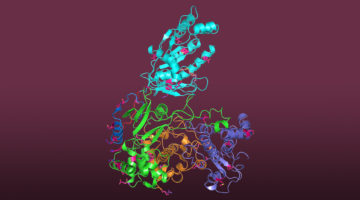
Targeting Bacteria That Cause Meningitis and Sepsis
Researchers determined the structure of a human antibody that broadly protects against a bacterium that causes meningitis and sepsis. The work provides molecular-level information about how the antibody confers broad immunity against a variable target and suggests strategies for further improvement of available vaccines. Read more »![]()
![]()
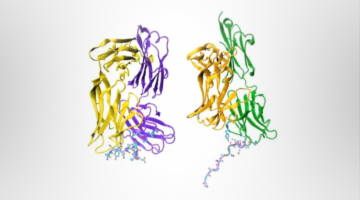
Structures Reveal New Target for Malaria Vaccine
Researchers isolated human-derived antibodies that protect against malaria, and protein-structure studies revealed the antibodies’ site of attack. The discovery paves the way for the development of a more effective and practical human vaccine for malaria, which is responsible for half a million deaths every year. Read more »![]()
![]()
Respiratory Virus Study Points to Likely Vaccine Target
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes serious respiratory disease in infants and older adults, but no vaccine is yet available. Researchers have now determined the molecular structures of human antibodies bound to an RSV surface protein, providing a promising route for designing a vaccine effective against a broad range of RSV strains. Read more »![]()
![]()
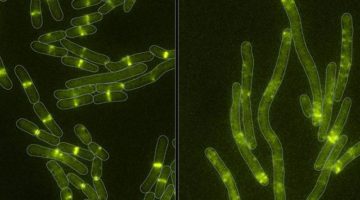
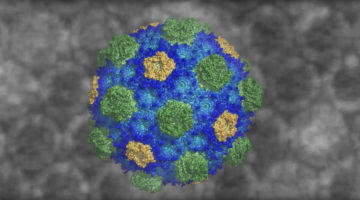
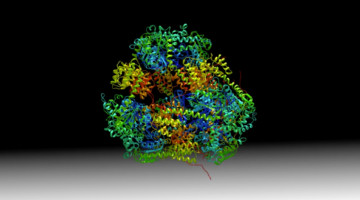
A Bacterial Jigsaw Puzzle Is Solved
Bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) are hollow protein shells that encapsulate enzymes involved in bacterial metabolism. Crystallography studies have provided atomic-resolution views of a fully assembled BMC, revealing basic principles of shell construction for fighting pathogens or bioengineering applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Structure of a Key Protein from the Zika Virus
The Zika virus (ZIKV) is a mosquito-borne pathogen recently linked to birth defects in infants. At the ALS, researchers have resolved the structure of a key ZIKV protein to 3.0 Å, an important step toward the rational design of drugs capable of disrupting viral functions and halting the spread of the disease. Read more »![]()
![]()
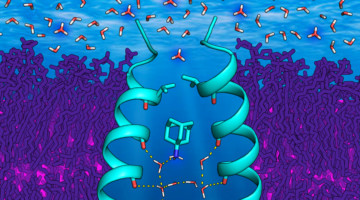
A Hollow Pyramid Unlocks Principles of Protein Architecture
Researchers have designed a hollow, pyramid-shaped protein with a controllable cavity size that could be useful in the capture and release of smaller compounds. The tools and techniques developed could be useful in analyzing and optimizing designed protein assemblies and understanding their behavior in solution. Read more »