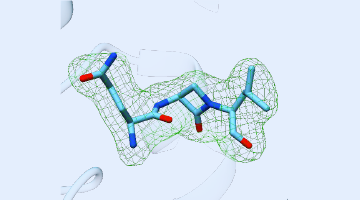
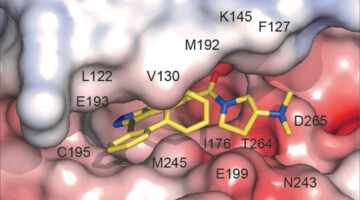
Using ALS beamlines, a new study revealed how CMX410 inhibits Pks13, a cell wall enzyme in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium responsible for tuberculosis. CMX410 is effective against drug-sensitive and drug-resistant strains of the bacterium and has been proven safe in multiple animal models of infection. Read more »![]()
![]()
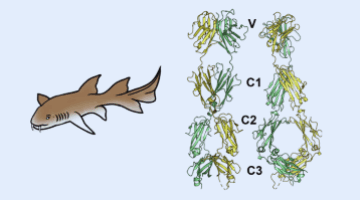
Sharks Shed Light on Origins of Adaptive Immune System
A team of researchers identified the three-dimensional structure of a protein expressed by a gene of a modern nurse shark that is proposed to be a close homologue to a gene that, more than 500 million years ago, gave rise to the adaptive immune system shared by all vertebrates. By understanding the emergence and evolution of the immune system, researchers may advance work in immunology, genetics, and biotechnology.
Read more »![]()
![]()
Identification of Structurally Novel KRASG12C Inhibitors through Covalent DNA-Encoded Library Screening
DNA-encoded library (DEL) technology was used to prepare a ~1.6 × 107-compound cysteine-reactive library (representative component shown at bottom, cysteine-reactive site indicated). Screening this library against the KRASG12C oncoprotein identified multiple structurally novel inhibitors of this challenging-to-drug target (e.g., frontmost green compound in the X-ray structure at right, covalent bond to KRASG12C indicated). Read more »
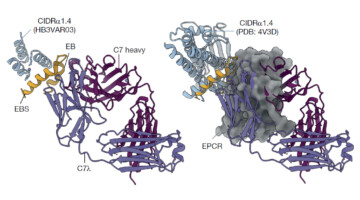
Identification and Structural Characterization of Antibodies for Severe Malaria
Researchers used x-ray crystallography at the ALS to characterize how two newly discovered antibodies prevent the protein interactions responsible for severe malaria. Understanding this mechanism offers novel insights for vaccine development. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Macromolecular Scaffold for Probing Actinium Chemistry
By encapsulating actinium atoms within a macromolecular complex for analysis using protein crystallography, researchers discovered that actinium has a unique solid-state bonding configuration. A better understanding of actinium behavior could help improve a promising cancer treatment known as targeted alpha therapy. Read more »![]()
![]()
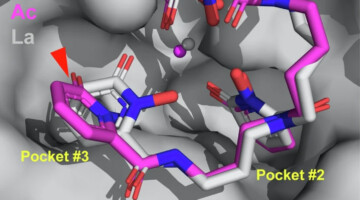
A Promising Compound for Reversible Male Contraception
Researchers found that a small-molecule protein inhibitor—screened from billions of compounds and analyzed using structural insights from protein crystallography—reversibly suppresses male fertility in mice. The work addresses the pressing need for more contraceptive options that enable all individuals to control their own fertility. Read more »![]()
![]()
Caught in the Actinium
In this work, researchers demonstrated a macromolecular scaffold that combines an 8-coordinate synthetic ligand and a mammalian protein to characterize the solution and solid-state behavior of the longest-lived actinium isotope. The information could help design better cancer treatments. Read more »
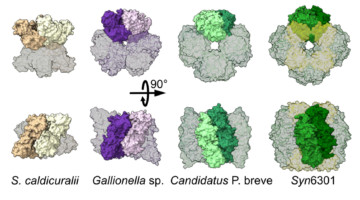
Protein Assemblies Show Surprising Variability
Protein-structure studies performed in part at the ALS helped researchers discover that the protein assemblies in a key carbon-cycling enzyme can rearrange with surprising ease. The findings raise the prospect of genetically tuning the protein in agricultural plant species to produce more productive and resource-efficient crops. Read more »![]()
![]()
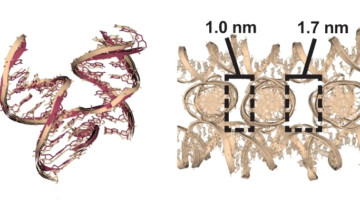
An Expanded Set of DNA Building Blocks for 3D Lattices
Researchers studied 36 DNA-based molecular junctions and discovered factors that yield superior self-assembled 3D lattice structures. The work expands the set of building blocks for lattices that can scaffold molecules into regular arrays, from proteins for structure studies to nanoparticles for nano-antennas and single-particle sensors. Read more »![]()
![]()
Protein Structures Aren’t Set in Stone
A group of researchers studying the world’s most abundant protein, an enzyme involved in photosynthesis called rubisco, showed how evolution can lead to a surprising diversity of molecular assemblies that all accomplish the same task. The findings reveal the possibility that many of the proteins we thought we knew actually exist in other, unknown shapes. Read more »
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 6
- Next Page »