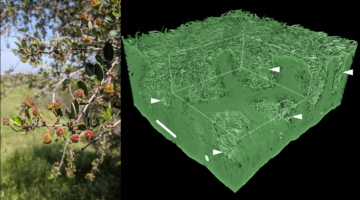
Many species of California lilac grow throughout the state, north to Humboldt and south to San Diego. Some species have developed an adaptation for arid climates: the stomatal crypt. This extremely rare anatomy intrigued a group of researchers, who characterized species with these crypts at the ALS. Their microtomography characterization revealed how the stomatal crypt helps plants survive drought. Read more »
Native American Interns Explore Engineering Opportunities at the Lab
This last summer, Berkeley Lab hosted three students from Navajo Technical University in a DOE-funded initiative that partners national labs with learning institutions whose populations are historically underrepresented in science. The goal is to increase enrollment of Native American students in Navajo Tech engineering programs. Read more »
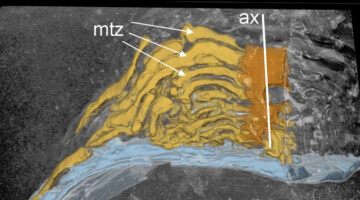
The Spatial Dynamics of Bone Remodeling During Lactation
To mobilize the minerals needed for milk production, osteocytes—the cells responsible for maintaining bone quality—facilitate the release of calcium and other minerals from the bone matrix surrounding them. In this study, researchers investigated how osteocytes balance the rapid release of calcium with maintaining bone integrity. Read more »![]()
Pacific Kelp Forests Are Far Older than We Thought
Researchers scanned newly discovered kelp fossils using x-ray tomography at the ALS. The images provided morphological information about the ancient kelp and, along with isotopic analyses, provided insights into the evolutionary history of northeastern Pacific Ocean kelp forests, which flourished more than 32 million years ago. Read more »
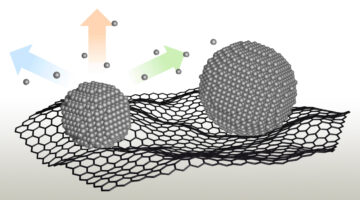
Tracking Platinum Movement on Fuel-Cell Electrodes
Researchers tracked the movement of the platinum nanoparticles that catalyze reactions in polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs) and correlated this movement with nanoparticle degradation. The results yielded solutions that can immediately reduce platinum waste in emission-free heavy-duty fuel-cell vehicles. Read more »![]()
![]()
Why Do Batteries Sometimes Catch Fire and Explode?
In order to better understand how a resting battery might undergo thermal runaway after fast charging, scientists are using a technique called “operando x-ray microtomography” to measure changes in the state of charge at the particle level inside a lithium-ion battery after it’s been charged. Read more »
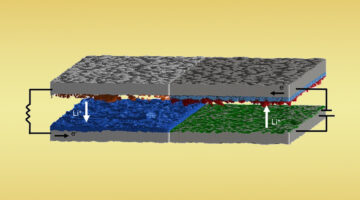
Internal Currents in Lithium Batteries after Fast Charging
In lithium batteries after fast charging, researchers measured the persistence of internal currents and found that large local currents continue even after charging has stopped. The work uses hard x-ray 3D imaging in a novel way and sheds light on the causes of thermal runaway and the catastrophic failure of lithium batteries at rest. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Deep-Learning Analysis of Lithium-Plating Dynamics in Batteries
Lithium-metal solid-state batteries are a promising technology, but the deposition (plating) of lithium metal on electrode surfaces remains a significant technical hurdle. Here, researchers used micro-computed tomography data to train an artificial intelligence model to identify characteristics vital to improving battery performance. Read more »![]()
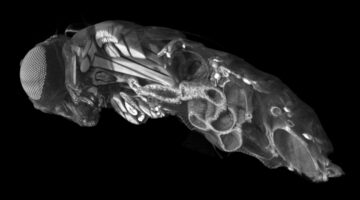
In Fruit-Fly Gut, Bacterial Niche Gets Remodeled for New Arrivals
Researchers found that fruit flies have a specialized niche in their digestive tracts that selects, maintains, and controls bacteria that benefit the fly. Colonization by one type of bacteria physically remodels the niche, promoting secondary colonization by unrelated bacteria. The results will help dissect the mechanisms of host-microbe symbiosis. Read more »
Structural organization of the spongy mesophyll
Many leaves have two layers of photosynthetic tissue: the palisade and spongy mesophyll. The latter is not well characterized and often treated as a random assemblage of irregularly shaped cells. These results show that simple principles may govern the organization and scaling of the spongy mesophyll in many plants and demonstrate the presence of structural patterns associated with leaf function. Read more »
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 6
- Next Page »