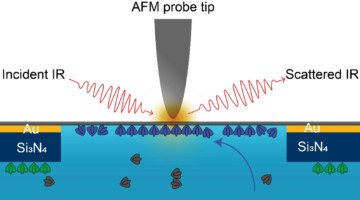
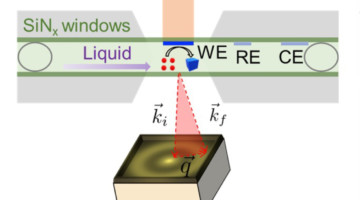
A new technique using infrared (IR) light revealed how the self-assembly of proteins is affected by environmental conditions in a surrounding liquid. This nanoscale probe of soft matter in a liquid matrix will facilitate advances in biology, plastics processing, and energy-relevant applications such as electrocatalysts and batteries. Read more »![]()
![]()
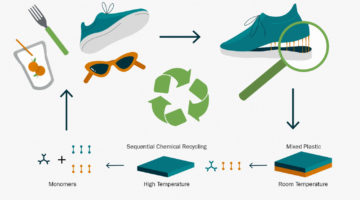
A New Material System for Mixed-Plastic Recycling
Scientists have designed a new material system to overcome one of the biggest challenges in recycling consumer products: mixed-plastic recycling. Their achievement will help enable a much broader range of fully recyclable plastic products and brings into reach an efficient circular economy for durable goods like automobiles. Read more »
Scientists Grow Lead-Free Solar Material With a Built-In Switch
A new ferroelectric material—grown in the lab from cesium germanium tribromide (CGB)—opens the door to an easier approach to making solar cell devices. Unlike conventional solar materials, CGB crystals are inherently polarized, where one side of the crystal builds up positive charges and the other side builds up negative charges, no doping required. Read more »
Multilayer Stack Opens Door to Low-Power Electronics
Researchers found that a multilayer stack of ultrathin materials exhibits a phenomenon called negative capacitance, which reduces the voltage required for transistor operation. The material is fully compatible with today’s silicon-based technology and is capable of reducing power consumption without sacrificing transistor size or performance. Read more »![]()
![]()
Ionic Conduction Mechanism and Design of Metal–Organic Framework Based Quasi-Solid-State Electrolytes
This cover image demonstrates the critical role of the solvent in the ion motion of intrinsically anionic metal–organic framework (MOF)–based quasi-solid-state electrolytes (QSSEs). Using hybrid theoretical and experimental approaches, we have identified solvent-assisted hopping as the dominant pathway for Li+ conduction in such materials, exemplified by MOF-688. Read more »
Operando Study of CO2 Reduction by Copper Nanoparticles
Since copper is necessary to catalyze the reduction of CO2, a greenhouse gas, to valuable products, scientists are working hard to improve its selectivity and activity. Now, researchers have developed an operando capability that can help in this effort by simultaneously probing chemical valence and interparticle dynamics. Read more »
Designer Materials to Keep Plastic Out of Landfills
Scientists have designed a new material system to overcome one of the biggest challenges in recycling consumer products: mixed-plastic recycling. Their achievement will help enable a much broader range of fully recyclable plastic products and brings into reach an efficient circular economy for durable goods like automobiles. Read more »
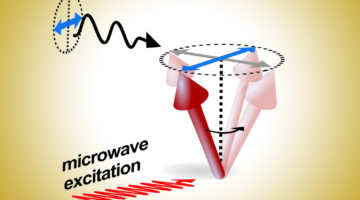
Dynamic Measurements of Antiferromagnetically Aligned Spins
Researchers developed a technique that enables time-resolved, direct detection of spin currents in either ferromagnetic or antiferromagnetic materials at GHz frequencies. Studying the dynamic properties of antiferromagnetic spintronic effects could lead to greater stability and faster intrinsic switching speeds compared to conventional spintronics. Read more »
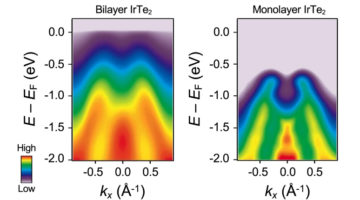
A Novel Insulating State Emerges in a 2D Material
Researchers found a unique insulating state in an atomically thin material, driven by the combined effects of lattice–charge interactions and atomic-bond formation. The work provides a better understanding of charge ordering in two-dimensional materials and opens up new possibilities for achieving designer electronic properties. Read more »![]()
![]()
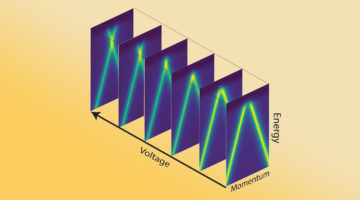
What Drives Electron–Hole Asymmetry in Graphene?
Using the ALS, researchers determined that interactions between electrons are what give rise to the divergent effects observed when graphene is doped with electrons versus holes. A better understanding of this electron–hole asymmetry could lead to new avenues for generating exotic material phases, including unconventional superconductivity. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- …
- 7
- Next Page »