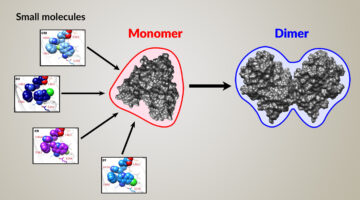
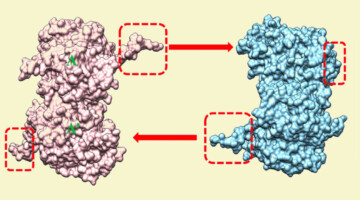
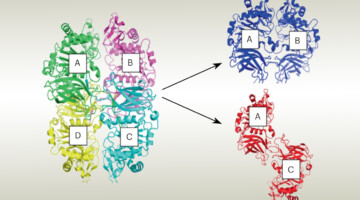
Researchers found that a small-molecule protein inhibitor—screened from billions of compounds and analyzed using structural insights from protein crystallography—reversibly suppresses male fertility in mice. The work addresses the pressing need for more contraceptive options that enable all individuals to control their own fertility. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Work Using Protein Crystallography
Protein crystallography is used for determining the molecular structure of proteins. Crystallized protein molecules cause a beam of incident x-rays to scatter in many directions, with constructive and destructive interference generating a diffraction pattern. By analyzing these patterns, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal and thus determine the protein's structure.
Time-Resolved SAXS Screen of Small-Molecule Drug Candidates
Time-resolved, high-throughput, small-angle x-ray scattering improved the screening of small-molecule drug candidates, providing insight into how they stimulate structural transitions in protein targets. The work will speed the discovery of treatments designed to activate biomolecular dynamics associated with desired therapeutic outcomes. Read more »![]()
![]()
Mechanistic Insight into a Viral-Factory Component
Recent protein-structure studies conducted at the ALS provided mechanistic insights into the function of a protein (σNS) involved in viral replication. Understanding these mechanisms will foster the development of therapeutic strategies against viruses that use σNS-like proteins to replicate. Read more »
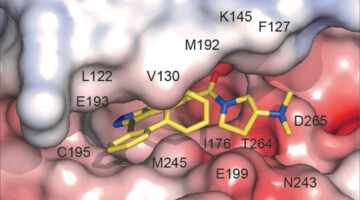
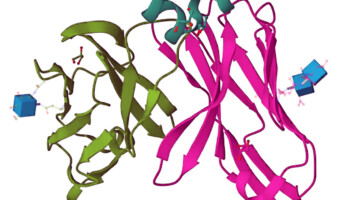
Novel modifications of PARP inhibitor veliparib increase PARP1 binding to DNA breaks
The catalytic activity of PARP1 is associated with DNA damage detection and repair among other cellular functions. We describe efforts to modify the allosteric properties of veliparib, a potent catalytic inhibitor of PARP1. These compounds highlight a unique way to trigger PARP1 retention on DNA breaks and open a path to unveil the pharmacological benefits of such inhibitors with novel properties. Read more »
Computer-Aided Protein Design for New Biomaterials
Using a computer-based approach, researchers designed porous protein crystals that were revealed to be stable, tunable, and atomically accurate using x-ray scattering and diffraction at the ALS. The work provides a powerful new platform for biological materials engineering and opens up wide applications in biotechnology and medicine. Read more »![]()
![]()
Precisely patterned nanofibres made from extendable protein multiplexes
Superhelical symmetry can be found in helical repeat proteins, and de novo helical repeat proteins are rigid and amenable to stacking in a head-to-tail fashion, which is an important factor in building up coincident symmetries. Now, using cyclic helical repeat proteins, Baker and colleagues generate protein nanostructures—as depicted on the cover—with coincident cyclic and superhelical symmetry axes. Read more »
Allosteric Tuning of Caspase-7: Establishing the Nexus of Structure and Catalytic Power
How can allosteric sites be more effectively targeted by small-molecule drugs? Using an integrated in vitro/in silico experimental workflow; we discovered novel allosteric inhibitors of caspase-7 and revealed new connections between the active site and the remote allosteric site (i. e., allosteric structure–activity relationships, ASARs) for this valuable disease target. Read more »
Plant Enzyme Builds Polymers That Fortify Cell Walls
With data obtained at the ALS, researchers gained insight into how an enzyme orchestrates the synthesis of a pectin polymer that imparts strength and flexibility to plant cell walls. The work could lead to improved biofuel production and guide the design of polymers with tailored functionalities for industrial or biomedical applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
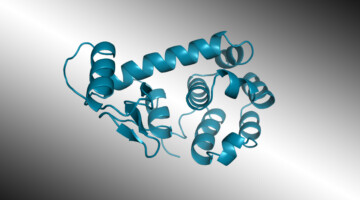
Gemini Beamline 2.0.1 Banks Its First Protein Structure
A protein structure obtained from ALS Beamline 2.0.1 (“Gemini”) has recently been published in the literature and deposited into the Protein Data Bank (PDB)—two significant firsts for this beamline. The structure helped provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms involved in triggering certain inflammatory diseases. Read more »
Chatbot-Style AI Designs Novel Functional Protein
Researchers used an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm, similar to those used in natural-language (“chatbot”) models, to design a functional protein that was then structurally validated at the ALS. The work could speed the development of novel proteins for almost anything from therapeutics to degrading plastic. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- …
- 15
- Next Page »