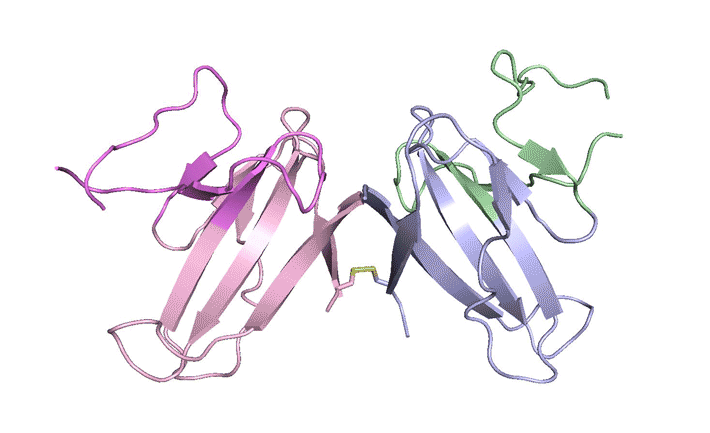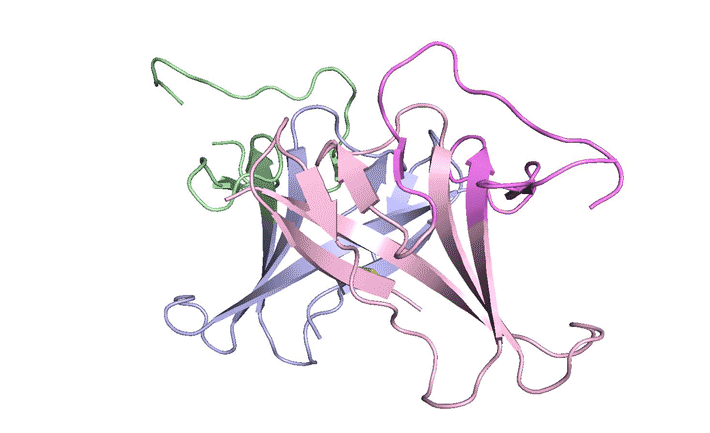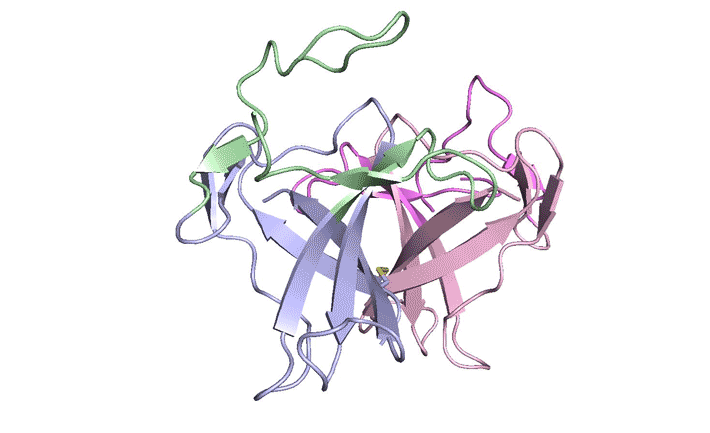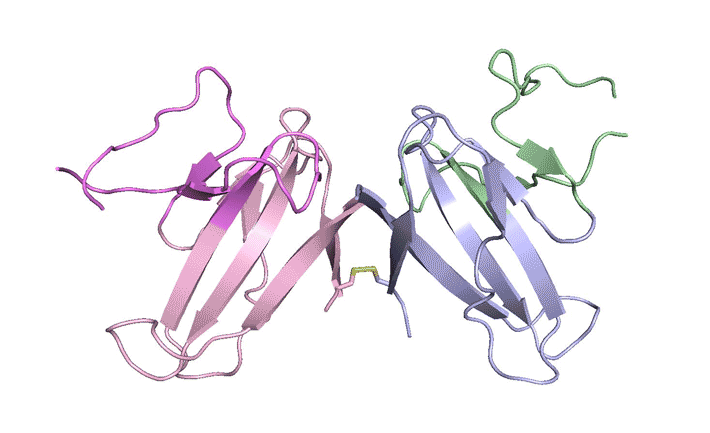
LONP1 is an AAA+ protease that maintains mitochondrial homeostasis by removing damaged or misfolded proteins. Elevated activity and expression promotes cancer cell proliferation and resistance to apoptosis-inducing reagents. Herein, we report the development of selective boronic acid-based LONP1 inhibitors using structure-based drug design as well as the first structures of human LONP1 bound to various inhibitors. Read more »
ALS Work Using Protein Crystallography
Protein crystallography is used for determining the molecular structure of proteins. Crystallized protein molecules cause a beam of incident x-rays to scatter in many directions, with constructive and destructive interference generating a diffraction pattern. By analyzing these patterns, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal and thus determine the protein's structure.
Targeting KRAS Mutant Cancers via Combination Treatment: Discovery of a 5-Fluoro-4-(3H)-quinazolinone Aryl Urea pan-RAF Kinase Inhibitor
The cover feature shows a chessboard (representative of KRAS mutant cells) and how the concerted action of the MEK inhibitor cobimetinib (rook) and the new selective pan-RAF inhibitor GNE-0749 (queen) force the opposing king (phospho-ERK, the downstream signaling node of RAF and MEK) into checkmate. Read more »
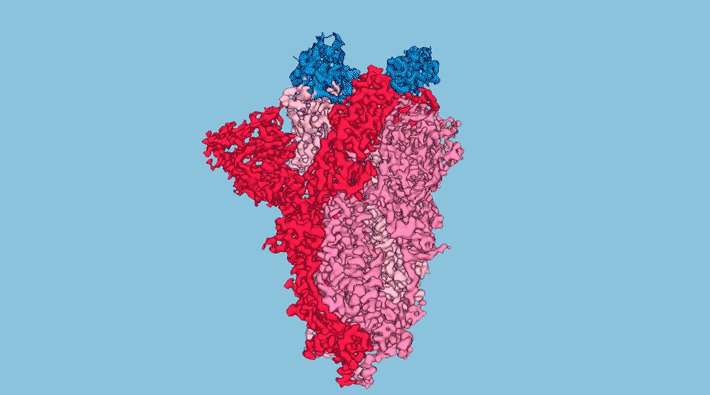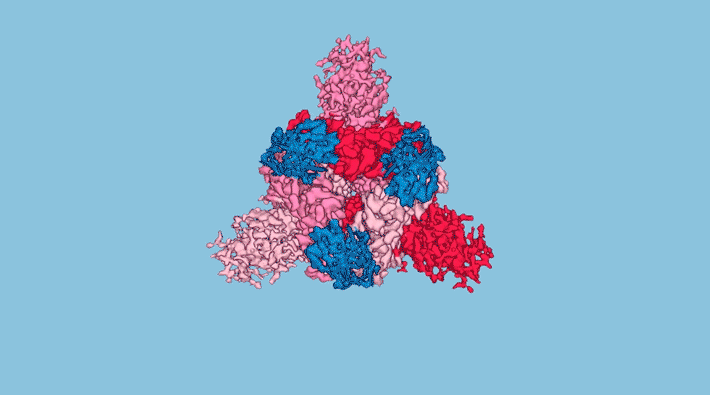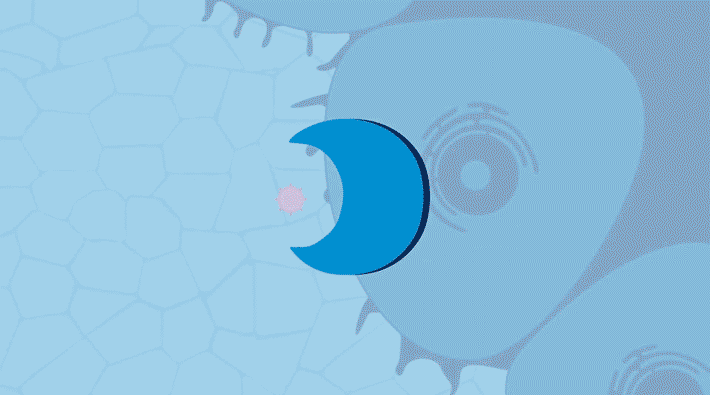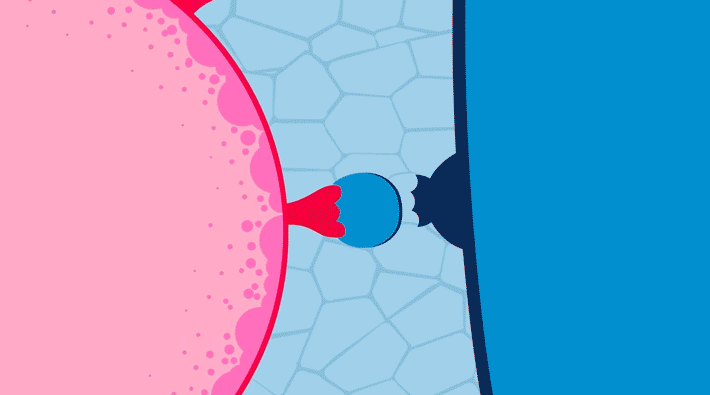
Mystery Protein Helps COVID–19 Avoid Immunity
Using the Advanced Light Source (ALS), researchers solved the structure of ORF8, a protein specific to SARS-CoV-2. Understanding the structure of ORF8 opens the door to therapy studies targeting SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for causing COVID-19. Read more »![]()
![]()
Construction, characterization and crystal structure of a fluorescent single-chain Fv chimera
In vitro display technologies based on phage and yeast have a successful history of selecting single-chain variable fragment (scFv) antibodies against various targets. However, single-chain antibodies are often unstable and poorly expressed. We explore the feasibility of converting scFv antibodies to an intrinsically fluorescent format by inserting a monomeric, stable fluorescent protein between the light- and heavy-chain variable regions. Read more »
CC-90009, a novel cereblon E3 ligase modulator, targets acute myeloid leukemia blasts and leukemia stem cells
A number of clinically validated drugs have been developed by repurposing the CUL4-DDB1-CRBN-RBX1 (CRL4CRBN) E3 ubiquitin ligase complex with molecular glue degraders to eliminate disease-driving proteins. Here, we present the identification of a first-in-class GSPT1-selective cereblon E3 ligase modulator, CC-90009, that targets acute myeloid leukemia blasts and leukemia stem cells. Read more »
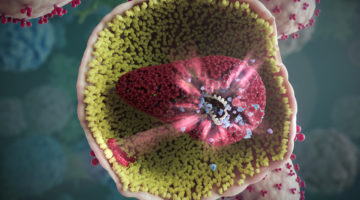
Inhalable COVID-19 Protection via Synthetic Nanobodies
Protein structures obtained in part at the ALS helped researchers to increase the potency of simplified antibodies (nanobodies) designed to neutralize SARS-CoV-2. Stable enough to be used in inhalers or nasal sprays, the nanobodies offer a new option, aside from injected vaccines, for COVID-19 prevention and treatment. Read more »![]()
![]()
The Odd Structure of ORF8: Scientists Map the Coronavirus Protein Linked to Immune Evasion and Disease Severity
Researchers determined the atomic structure of a coronavirus protein thought to help the pathogen evade and dampen response from human immune cells. Researchers determined the atomic structure of a coronavirus protein thought to help the pathogen evade and dampen response from human immune cells. Read more »
Newly Discovered Photosynthesis Enzyme Yields Evolutionary Clues
Scientists have discovered a primitive form of rubisco, a photosynthesis enzyme that has helped shape life on Earth. Detailed information about its structure, determined using complementary techniques at the ALS, will help scientists understand how carbon-fixing organisms oxygenated the atmosphere and how modern plants evolved. Read more »
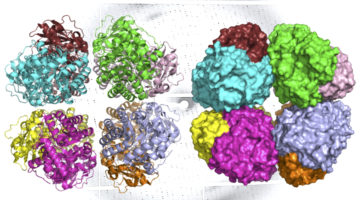
Domain-Swap Dimerization of Acanthamoeba castellanii CYP51 and a Unique Mechanism of Inactivation by Isavuconazole
We investigated the mechanism of action of antifungal drugs in the human pathogen Acanthamoeba castellanii. We discovered that the enzyme target formed a dimer via an N-termini swap, whereas drug-bound AcCYP51 was monomeric. Cover image shows a molecular model of the AcCYP51 dimer in a phospholipid bilayer. Read more »
Experimental Drug Targets HIV in a Novel Way
Researchers from Gilead Sciences Inc. solved the structure of an experimental HIV drug bound to a novel target: the capsid protein that forms a shield around the viral RNA. The work could lead to a long-lasting HIV treatment that overcomes the problem of drug resistance and avoids the need for burdensome daily pill-taking. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- …
- 15
- Next Page »