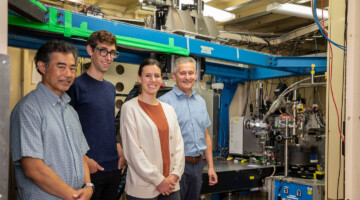
In this work, researchers demonstrated a macromolecular scaffold that combines an 8-coordinate synthetic ligand and a mammalian protein to characterize the solution and solid-state behavior of the longest-lived actinium isotope. The information could help design better cancer treatments. Read more »
ALS Work Using Scattering/Diffraction
These techniques make use of the patterns of light produced when x-rays are deflected by the closely spaced lattice of atoms in solids and are commonly used to determine the structures of crystals and large molecules such as proteins.
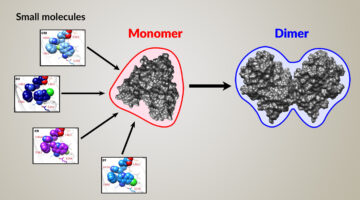
Engineered π⋯π interactions favour supramolecular dimers X@[FeL3]2(X = Cl, Br, I): solid state and solution structure
Intermolecular interactions drive the formation of biological supramolecular architectures, inspiring the design of artificial supramolecular assemblies and molecular machines. Here, the engineering of supramolecular interactions allows selection of a self-recognition process of dimerization over one of helicate-cage formation. Read more »
Double-Helical Tiled Chain Structure of the Twist-Bend Liquid Crystal Phase in CB7CB
The structure of the twist-bend (TB) phase of the bent dimer CB7CB and its mixtures with 5CB is characterized, revealing a hidden invariance of the self-assembly of the TB structure. Remarkably, the distance along the length for a single turn of this helix is given by 2πRmol, where Rmol is the radius of the bend curvature of a single all-trans CB7CB molecule. Read more »
Time-Resolved SAXS Screen of Small-Molecule Drug Candidates
Time-resolved, high-throughput, small-angle x-ray scattering improved the screening of small-molecule drug candidates, providing insight into how they stimulate structural transitions in protein targets. The work will speed the discovery of treatments designed to activate biomolecular dynamics associated with desired therapeutic outcomes. Read more »![]()
![]()
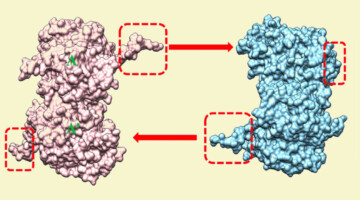
Mechanistic Insight into a Viral-Factory Component
Recent protein-structure studies conducted at the ALS provided mechanistic insights into the function of a protein (σNS) involved in viral replication. Understanding these mechanisms will foster the development of therapeutic strategies against viruses that use σNS-like proteins to replicate. Read more »
Engineering Lipophilic Aggregation of Adapalene and Adamantane-Based Cocrystals via van der Waals Forces and Hydrogen Bonding
Adamantanes are emerging building blocks for active pharmaceutical ingredients. In this work, we sought to understand how systematic modification of the hydrophobic cage in adamantanes could result in changes to crystal packing in single and multicomponent organic solids. Read more »
Superhard Materials at the Nanoscale: Smaller is Better
In the superhard material, rhenium diboride, smaller grain size leads to greater yield strength (i.e., the amount of stress tolerated before permanent deformation). Because such transition-metal borides are extremely hard, metallic, and can be synthesized at ambient pressure, they have exciting potential for use in next-generation cutting tools. Read more »![]()
![]()
Two-dimensional perovskite templates for durable, efficient formamidinium perovskite solar cells
When the lattice-matched 2D perovskite BA2FAPb2I7 (red) is incorporated into a yellow-phase FAPbI3 matrix (yellow), the 2D crystallites present a perovskite-like surface, which serves as a template for the FAPbI3 to convert to its photoactive phase (black). The resulting phase-stabilized FAPbI3 shows substantially improved optoelectronic properties and exceptional stability under 85°C and sunlight. Read more »
A Novel Staircase Pattern in Spin-Stripe Periodicity
Striped patterns of spins in a magnetic thin film were found to evolve under an applied magnetic field in steps reminiscent of a structure known as the “Devil’s Staircase.” Such studies are valuable for understanding competing interactions at the atomic level for applications such as magnetic sensors and spintronic devices. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Cleaner Way to Produce Ammonia
A cavity made from linked rare-earth metals, such as zirconium and titanium, can convert abundant molecular nitrogen (N2) into useful nitrogen compounds, including ammonia or tris(silyl)amines, at room temperature. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- …
- 39
- Next Page »