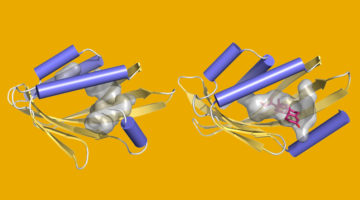
Using the computer game, “Foldit,” nonexpert citizen scientists designed new proteins whose structures, verified at the ALS, were equivalent in quality to and more structurally diverse than computer-generated designs. The work shows the potential of using crowd-based creativity in the design of new proteins for fighting illness and disease. Read more »![]()
![]()
Self-Assembling 2D Arrays with de Novo Protein Building Blocks
Modular self-assembly of biomolecules in two dimensions (2D) is straightforward with DNA but has been difficult to realize with proteins, due to the lack of modular specificity similar to Watson–Crick base pairing. Here, researchers describe a general approach to designing 2D arrays using de novo designed pseudosymmetric protein building blocks. Read more »
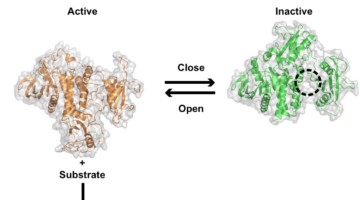
Locking Protein Structure to Close the Door on Cancer
While the SHP2 protein helps regulate cellular activity, mutations in its structure can lead to cancer. X-ray crystallography at the ALS and SSRL has revealed differences between normal and mutated SHP2, as well as how it binds to certain cancer drugs. These structural insights open the door to new types of cancer therapy. Read more »
Scientists Capture Photosynthesis in Unprecedented Detail
Scientists have captured a more detailed picture than ever of the steps in photosynthesis, the process by which plants use sunlight to split water and produce oxygen while making the carbohydrates that sustain life on Earth. The idea is eventually to have a continuous movie of how water is split into oxygen, and how plants do that using sunlight. Read more »
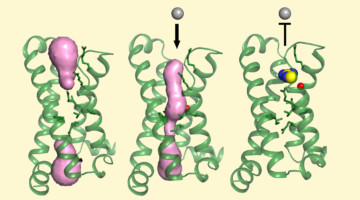
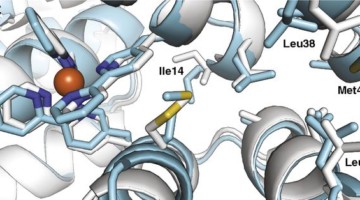
Structure Reveals Mechanism Behind Periodic Paralysis
X-ray crystallography of a membrane protein provided a structural understanding of how a single mutation can result in periodic muscle paralysis. The results suggest possible drug designs that could provide relief to patients with a genetic disorder that causes them to be overcome suddenly with profound muscle weakness. Read more »![]()
![]()
NIH Grant Will Enhance Structural Biology Research Experience for ALS Users
A recently awarded National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant will help integrate existing structural biology resources at the ALS to better serve users. The funds will help establish a centralized collaborative mechanism, called ALS-ENABLE, that will guide users through the most appropriate routes for answering their biological questions. Read more »
Exploring the Roots of Photosynthesis in a Soil-Dwelling Bacterium
The bacterium, H. modesticaldum, is thought to have a photosynthetic reaction center resembling the earliest common ancestor of all photosynthesis complexes. Its molecular structure has now been solved, providing insight into the evolution of photosynthesis and how nature optimized light-driven energy collection. Read more »
Bending the (β-Sheet) Curve to Shape Protein Cavities
Curved β sheets are basic building blocks of many protein cavities that, by serving as binding sites for other molecules, are essential to protein function. β-sheet curvature can now be controlled with atomic-level accuracy, opening the door to custom-designed sites capable of entirely new functions. Read more »![]()
![]()
NCAA Drives Formation of Designed Proteins
A noncanonical amino-acid (NCAA) complex has been found to drive the self-assembly of a computationally designed protein. Bpy-ala, which is “noncanonical” because it’s not among the 20 amino acids that occur naturally, has useful properties that could be used to generate novel photoactive proteins. Read more »
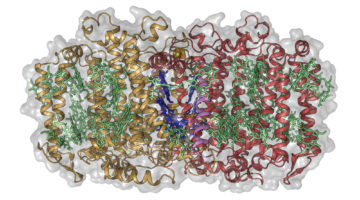
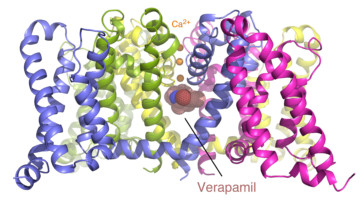
Two Basic Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Drugs
The structures of proteins controlling calcium-ion transport through cell membranes have been revealed, bound to two drugs known as calcium channel blockers. The discovery might accelerate the development of safer and more effective drugs for treating cardiovascular disorders such as high blood pressure, chest pain, and irregular heartbeat. Read more »![]()
![]()