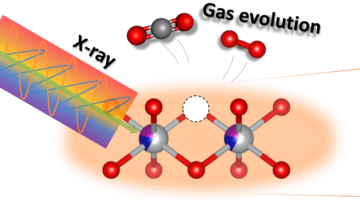
Researchers used soft x-ray resonant inelastic x-ray scattering at the ALS to understand the role of aluminum doping in improving the stability of commercially used cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Read more »
Industry@ALS
Studying Interfacial Effects in Solid-Electrolyte Batteries
An ambient-pressure probe of a solid electrolyte revealed how surface electrochemical mechanisms lead to poor electrolyte performance and battery failure. The results can help scientists engineer better coatings and interfaces, which are essential for building safer and better-performing batteries, particularly for use in vehicles. Read more »![]()
![]()
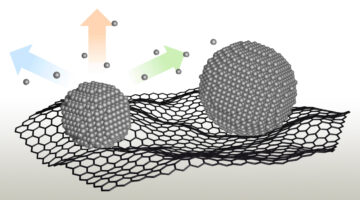
Tracking Platinum Movement on Fuel-Cell Electrodes
Researchers tracked the movement of the platinum nanoparticles that catalyze reactions in polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs) and correlated this movement with nanoparticle degradation. The results yielded solutions that can immediately reduce platinum waste in emission-free heavy-duty fuel-cell vehicles. Read more »![]()
![]()
“Computer Vision” Review of X-Ray Movies Leads to New Insights
Using a type of machine learning called “computer vision” to mine data from x-ray movies, researchers made new discoveries about the reactivity of a material in rechargeable batteries. The results suggest that optimizing the carbon layer thickness on the electrode surface could help researchers to design more efficient batteries. Read more »
How Structure Affects the Activity of Lipid Nanoparticles
Berkeley Lab and Genentech scientists related the internal structures of lipid nanoparticles to their efficacy at drug delivery, using a combination of methods including x-ray scattering at the ALS. The work promises to expedite the development of drug delivery systems for the treatment of diseases such as COVID-19 and cancer. Read more »![]()
![]()
Breaking Barriers in Drug Delivery with Better Lipid Nanoparticles
A collaboration between Berkeley Lab and Genentech, a member of the Roche Group, is working to break through some of the drug delivery bottlenecks by designing the most effective lipid nanoparticles (LNPs)—tiny spherical pouches made of fatty molecules that encapsulate therapeutic agents until they dock with cell membranes and release their contents. Read more »
Chatbot-Style AI Designs Novel Functional Protein
Researchers used an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm, similar to those used in natural-language (“chatbot”) models, to design a functional protein that was then structurally validated at the ALS. The work could speed the development of novel proteins for almost anything from therapeutics to degrading plastic. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Study on the Reaction Mechanism of a Model Organic Cathode in Magnesium-Ion Batteries
Battery and analytical studies of a model benzoquinone-type cathode reveal reversible structural transformations driven by a new precedence of a unique dissolution/precipitation mechanism and raise the question regarding its prevalence in other organic cathode batteries. Read more »
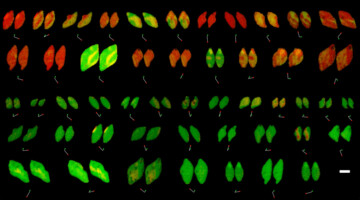
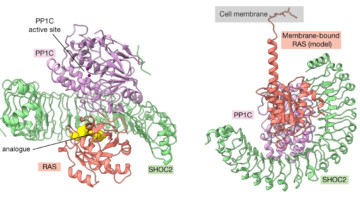
Structures Signal Fresh Targets for Anticancer Drugs
Researchers from Genentech used a suite of methods, including small-angle x-ray scattering, to learn how an assembly of three proteins works together to transmit signals for cell division. The work reveals new targets for the development of drugs that fight certain types of cancer, including lung, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer. Read more »![]()
![]()
Multilayer Stack Opens Door to Low-Power Electronics
Researchers found that a multilayer stack of ultrathin materials exhibits a phenomenon called negative capacitance, which reduces the voltage required for transistor operation. The material is fully compatible with today’s silicon-based technology and is capable of reducing power consumption without sacrificing transistor size or performance. Read more »![]()
![]()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 7
- Next Page »