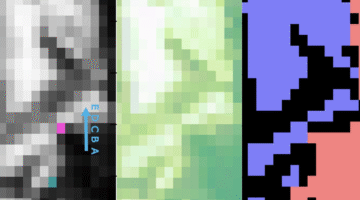
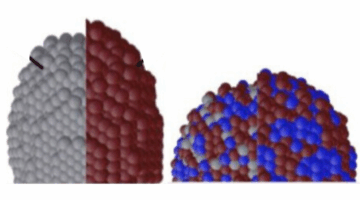
Machine learning tools and experiments at the ALS enabled the identification of defect-rich regions in single-crystalline Co3Sn2S2 that link to how surface electrons move. Atom-level understanding of how the surface electronic properties of a magnetic semimetal can be tuned could guide its use in advanced technologies like spintronics and catalysis. Read more »![]()
Science Highlights
Disrupting Cancer’s Broken Molecular Switch
Researchers identified a compound that disrupts a hard-to-target tumor growth pathway in breast, lung, and other cancers and used the ALS to characterize the chemical interactions critical to its potency. This work contributed to the development of a similar compound currently undergoing clinical trials in cancer patients, and informs hypotheses for designing better drug candidates. Read more »
Thin-Film Coating Boosts X-Ray Instrument Performance
Optimized thin films doubled the efficiency of gratings in x-ray experiments at the ALS. The atoms-thick copper and gold layers let the grooved surfaces deliver energy that had previously been lost to absorption in the diffraction gratings, which are key elements in x-ray spectroscopy. Read more »![]()
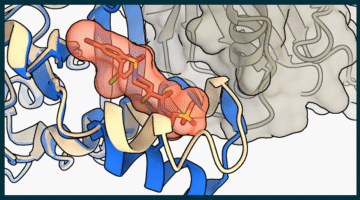
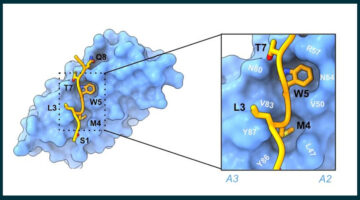
AI Delivers Rapid, Precise Design of Tumor-Targeting Protein
A new protein designed using AI can precisely recognize a key therapeutic target for cancer. X-ray crystallography data collected at the ALS confirmed the new protein’s specificity for its target, demonstrating a configurable and scalable approach to cancer therapy. Read more »![]()
Dynamic Surface Restructuring in Ag–Cu Boosts CO2 Conversion
Multimodal in situ x-ray experiments at the ALS revealed how copper–silver nanoparticle catalysts evolve during CO2 photoreduction. The findings, which demonstrate dynamic catalyst restructuring at the atomic level, provide crucial insights for enhancing the selectivity and efficiency of CO2 conversion into high-value chemicals. Read more »![]()
![]()
Ancient Asteroid Provides Evidence of Amino Acid Precursors
Researchers identified nitrogen-rich compounds in samples from the asteroid Bennu, returned to Earth by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission. The results support the idea that asteroids like Bennu may have delivered the essential chemical building blocks of life to Earth in the distant past. Read more »![]()
![]()
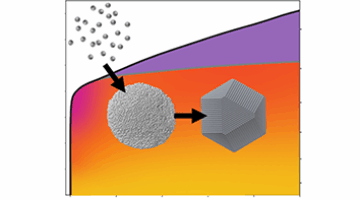
Building Materials from the Nanocrystal Up
Researchers used the Advanced Light Source to clarify how an unusual intermediate state accelerates the transformation of nanocrystals into a superlattice during a two-step process with fewer defects than a one-step process. Read more »![]()
![]()
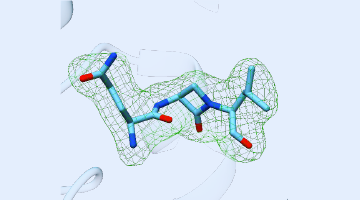
X-Rays Shed Light on Possible New Treatments for TB
Using ALS beamlines, a new study revealed how CMX410 inhibits Pks13, a cell wall enzyme in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium responsible for tuberculosis. CMX410 is effective against drug-sensitive and drug-resistant strains of the bacterium and has been proven safe in multiple animal models of infection. Read more »![]()
![]()
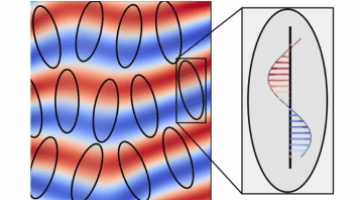
Nematic Magnetic Helices Fluctuate at Different Tempos
During a series of experiments at the ALS, researchers identified helical magnetic spins that fluctuate at different time scales during a phase transition as a function of temperature in a nematic iron germanium thin film. The results provide a framework for characterizing exotic phases, which may have interesting optical and transport properties for microelectronics and spintronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
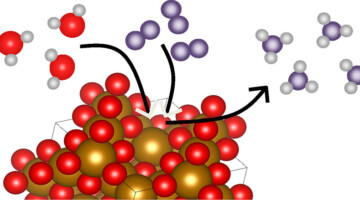
From Magnetite to Ammonia, A New Line of Production
Ammonia is a critical ingredient in many important industrial and agricultural applications. The Haber–Bosch process is the primary process for large-scale ammonia production. A new study uses an experimental–theoretical approach to uncover how interfacial chemistry at the magnetite–water interface drives ammonia synthesis under ambient temperature and pressure. Read more »![]()
![]()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 27
- Next Page »