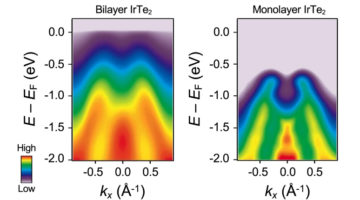
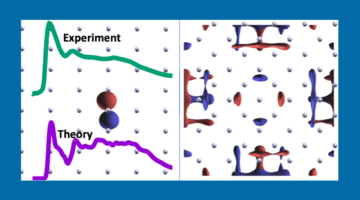
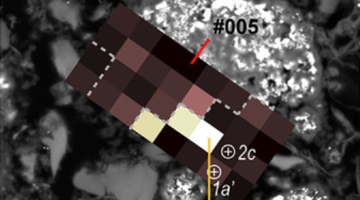
Researchers found a unique insulating state in an atomically thin material, driven by the combined effects of lattice–charge interactions and atomic-bond formation. The work provides a better understanding of charge ordering in two-dimensional materials and opens up new possibilities for achieving designer electronic properties. Read more »![]()
![]()
Science Highlights
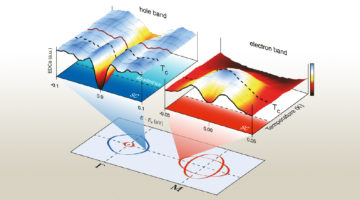
What Drives Electron–Hole Asymmetry in Graphene?
Using the ALS, researchers determined that interactions between electrons are what give rise to the divergent effects observed when graphene is doped with electrons versus holes. A better understanding of this electron–hole asymmetry could lead to new avenues for generating exotic material phases, including unconventional superconductivity. Read more »![]()
![]()
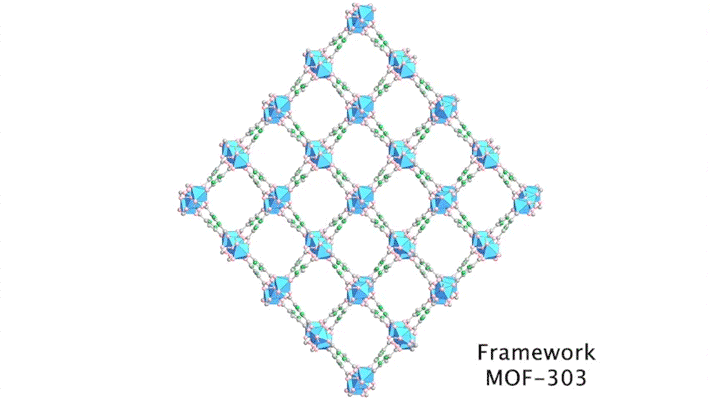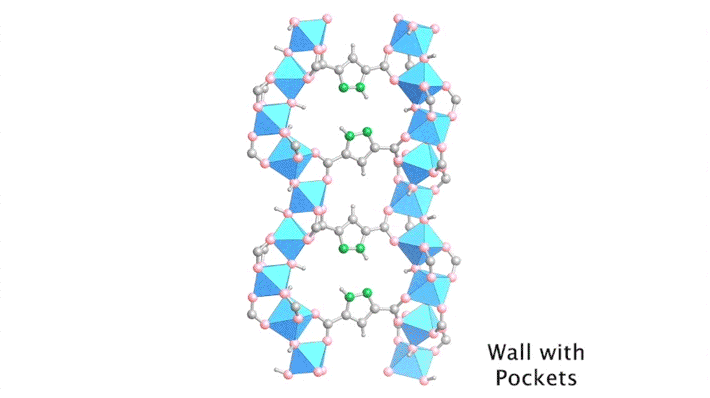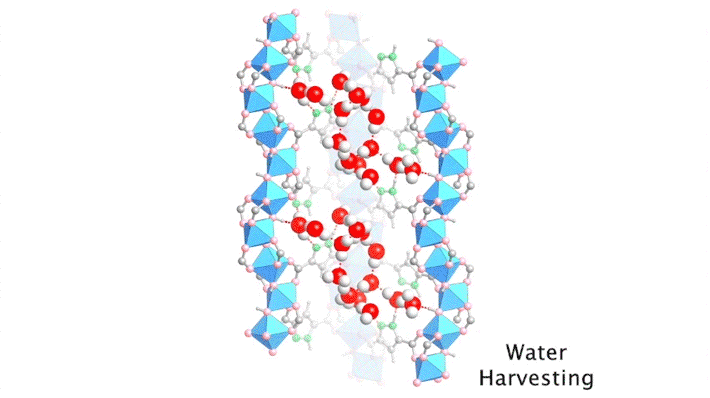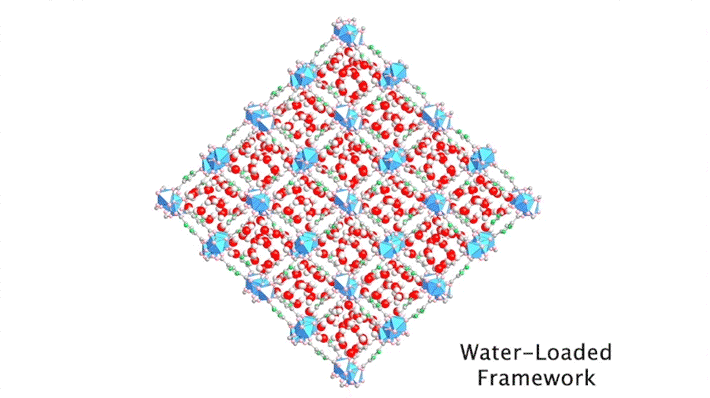
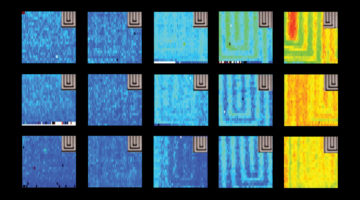
Improving the Efficiency of Atmospheric Water Harvesting
Researchers traced the step-by-step path of water-molecule uptake in a porous compound, then made pinpoint modifications to shape the material’s water-sorption behavior. The results led to improvements in the compound’s efficiency at harvesting water from the air, an important step toward alleviating water shortages in the future. Read more »![]()
![]()
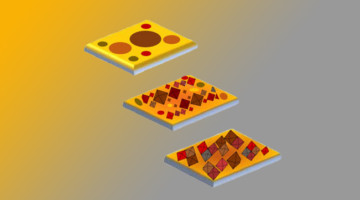
Interlayer Coupling Drives Mysterious Phase Transition
Researchers found that a mysterious phase transition in an iron-based superconductor is driven by interactions between the material’s 2D layers. The results counter the assumption that interlayer coupling is negligible in such materials, suggesting instead that the interactions can be an effective way to tune superconductivity. Read more »![]()
![]()
Revealing Lithium Metal’s Electronic Structure
Spectroscopy at the ALS and theoretical calculations at the Molecular Foundry revealed the intrinsic spectroscopic signature of lithium metal and explained the origin of previous contradictory reports. The findings provide a benchmark for further studies of lithium compounds towards batteries with higher capacity and energy density. Read more »![]()
![]()
Unexpected Transformations Reinforce Roman Architectural Concrete
Researchers used the ALS to study binding phases in Roman architectural concrete, revealing reactions and profound transformations that contribute to long-term cohesion and durability. The findings add to our growing understanding of cementing processes in Roman concretes, informing resilient materials of the future. Read more »![]()
![]()
Strategies for Reducing Platinum Waste in Fuel Cells
Industry and university researchers used the ALS to explore why the platinum used as a catalyst in hydrogen fuel cells degrades unevenly. The resulting knowledge has enabled the development of simple, effective strategies to reduce the waste of precious catalyst material, lowering the costs associated with a promising green technology. Read more »![]()
![]()
An Antibody That Broadly Neutralizes SARS-CoV-2
An antibody that appears to neutralize all known SARS-CoV-2 strains and closely related coronaviruses was discovered with the help of the ALS. The work highlights principles underlying antibody potency, breadth, and escapability that can guide the development of therapeutics against the current and potential future pandemics. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Split-Screen View of Solar-Cell Crystallization
Researchers simultaneously monitored both the structure and function of a photovoltaic material as it crystallized from solution. The work raises the prospect of rationally tuning materials for optimal performance in photovoltaics and other light-manipulating devices, including light-emitting diodes, detectors, and lasers. Read more »![]()
![]()
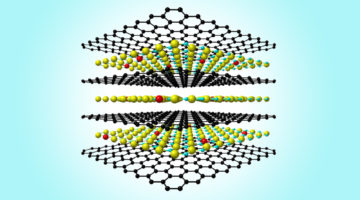
A Two-Dimensional Room-Temperature Magnet
Researchers have made the world’s thinnest (one atom thick) magnet that’s chemically stable under ambient conditions. The two-dimensional material, magnetically characterized at the ALS, could enable big advances in next-generation memory devices, computing, spintronics, and quantum physics. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- …
- 27
- Next Page »