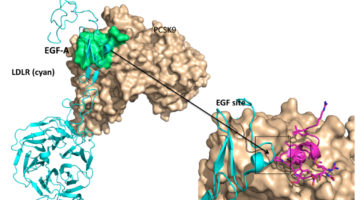
Genentech has been working in collaboration with the ALS for years with the goal of identifying a better cholesterol treatment mechanism that targets a cholesterol-regulating protein in the body known as PCSK9. Recent advances in understanding PCSK9’s structure have put them closer to that goal. Read more »![]()
ALS Work Using Protein Crystallography
Protein crystallography is used for determining the molecular structure of proteins. Crystallized protein molecules cause a beam of incident x-rays to scatter in many directions, with constructive and destructive interference generating a diffraction pattern. By analyzing these patterns, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal and thus determine the protein's structure.
NIH Grant Will Enhance Structural Biology Research Experience for ALS Users
A recently awarded National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant will help integrate existing structural biology resources at the ALS to better serve users. The funds will help establish a centralized collaborative mechanism, called ALS-ENABLE, that will guide users through the most appropriate routes for answering their biological questions. Read more »
Exploring the Roots of Photosynthesis in a Soil-Dwelling Bacterium
The bacterium, H. modesticaldum, is thought to have a photosynthetic reaction center resembling the earliest common ancestor of all photosynthesis complexes. Its molecular structure has now been solved, providing insight into the evolution of photosynthesis and how nature optimized light-driven energy collection. Read more »
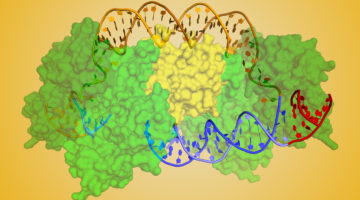
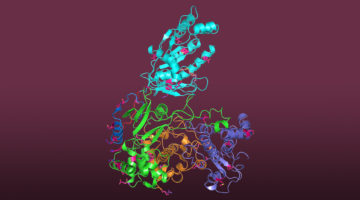
The CRISPR Target-Recognition Mechanism
CRISPR-associated (Cas) proteins have revolutionized gene editing by vastly simplifying the insertion of short snippets of new (“donor”) DNA into very specific locations of target DNA. Now, researchers have discovered how the Cas proteins are able to recognize the target locations with such great specificity. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Work Highlighted in DOE Top 40 Countdown
To celebrate DOE’s 40th anniversary (October 1, 2017), the Office of Science (SC) collected 40 scientific milestones from the previous 40 years, each one supported by SC. The ALS played a key role in two of the milestones: 2005 (ribosome) and 2009 (topological materials). Read more »
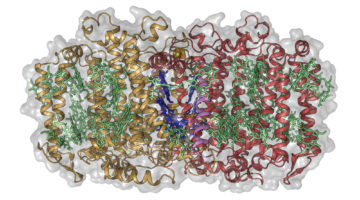
Global Blood Therapeutics Uses ALS to Tackle Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD), which affects millions of people worldwide, has traditionally been treated with a cytotoxic drug that has a range of negative side effects and variable patient response. Bay Area biopharmaceutical company Global Blood Therapeutics (GBT) is on a mission to develop a better treatment and is using the ALS to help. Read more »![]()
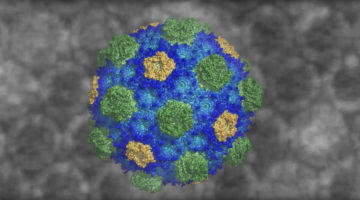
A Bacterial Jigsaw Puzzle Is Solved
Bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) are hollow protein shells that encapsulate enzymes involved in bacterial metabolism. Crystallography studies have provided atomic-resolution views of a fully assembled BMC, revealing basic principles of shell construction for fighting pathogens or bioengineering applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Structure of a Key Protein from the Zika Virus
The Zika virus (ZIKV) is a mosquito-borne pathogen recently linked to birth defects in infants. At the ALS, researchers have resolved the structure of a key ZIKV protein to 3.0 Å, an important step toward the rational design of drugs capable of disrupting viral functions and halting the spread of the disease. Read more »![]()
![]()
Study Sheds Light on How Bacterial Organelles Assemble
Scientists are providing the clearest view yet of an intact bacterial microcompartment (BMC), revealing the polyhedral structure and assembly of this organelle’s protein shell. Having the full structure can help provide important information in fighting pathogens or bioengineering bacterial organelles for beneficial purposes. Read more »
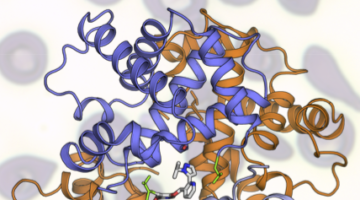
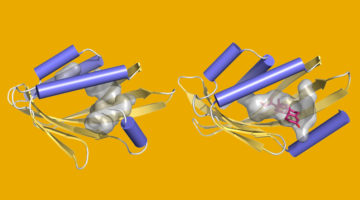
Bending the (β-Sheet) Curve to Shape Protein Cavities
Curved β sheets are basic building blocks of many protein cavities that, by serving as binding sites for other molecules, are essential to protein function. β-sheet curvature can now be controlled with atomic-level accuracy, opening the door to custom-designed sites capable of entirely new functions. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- …
- 15
- Next Page »