Using ALS beamlines, a new study revealed how CMX410 inhibits Pks13, a cell wall enzyme in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium responsible for tuberculosis. CMX410 is effective against drug-sensitive and drug-resistant strains of the bacterium and has been proven safe in multiple animal models of infection. Read more »![]()
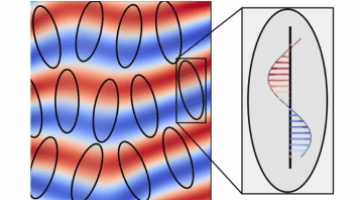
Nematic Magnetic Helices Fluctuate at Different Tempos
During a series of experiments at the ALS, researchers identified helical magnetic spins that fluctuate at different time scales during a phase transition as a function of temperature in a nematic iron germanium thin film. The results provide a framework for characterizing exotic phases, which may have interesting optical and transport properties for microelectronics and spintronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
From Magnetite to Ammonia, A New Line of Production
Ammonia is a critical ingredient in many important industrial and agricultural applications. The Haber–Bosch process is the primary process for large-scale ammonia production. A new study uses an experimental–theoretical approach to uncover how interfacial chemistry at the magnetite–water interface drives ammonia synthesis under ambient temperature and pressure. Read more »![]()
![]()
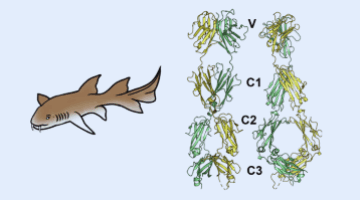
Sharks Shed Light on Origins of Adaptive Immune System
A team of researchers identified the three-dimensional structure of a protein expressed by a gene of a modern nurse shark that is proposed to be a close homologue to a gene that, more than 500 million years ago, gave rise to the adaptive immune system shared by all vertebrates. By understanding the emergence and evolution of the immune system, researchers may advance work in immunology, genetics, and biotechnology.
Read more »![]()
![]()
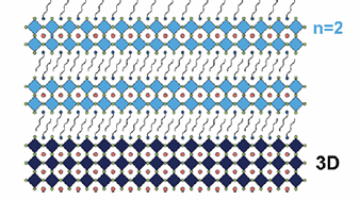
Stable 2D Interlayer Prolongs Perovskite Devices
Layered 2D/3D perovskite bilayer heterostructures have the potential to boost the performance and durability of many types of electronic and photonic devices, but maintaining this performance depends on the stability of the cell’s 2D interlayer. In this study, researchers optimized time-resolved, spontaneous thin-film deposition of 2D perovskites using a mixed solvent approach to produce phase pure, stable thin films with high crystallinity. Read more »![]()
![]()
A New Twist for Superconductivity in Bilayer Graphene
In a study of twisted bilayer graphene (TBG) systems, researchers found intriguing spectroscopic features in a superconducting “magic-angle” TBG—features that are absent in non-superconducting TBG. The results provide crucial information on superconductivity in magic-angle TBG for next-gen electronics and advanced energy technologies. Read more »![]()
![]()
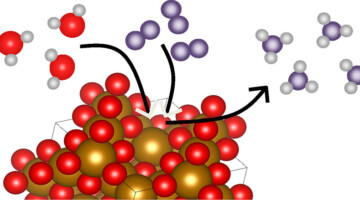
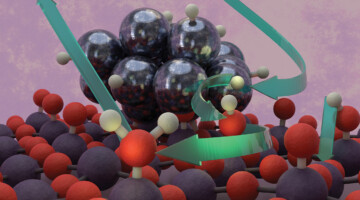
Catching “Hydrogen Spillover” onto a Catalytic Surface
Researchers uncovered the precise mechanism of hydrogen spillover (H2 splitting and migration) onto a catalytic surface by watching it happen under various conditions. The research lays the foundation for designing more efficient catalysts and storage materials essential for next-generation hydrogen energy technologies. Read more »![]()
![]()
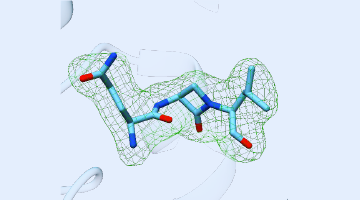
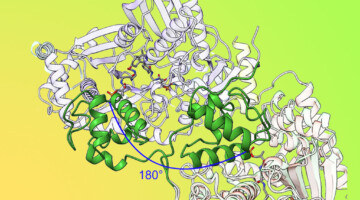
Deep-Dive Inspection of a Molecular Assembly Line
By locking down certain movable parts of a modular drug-building protein, researchers learned new details about how carrier proteins transfer the product protein between modules. The results offer insights that could enable scientists to design and create new and improved medicines, such as antibiotics, using synthetic biology. Read more »![]()
![]()
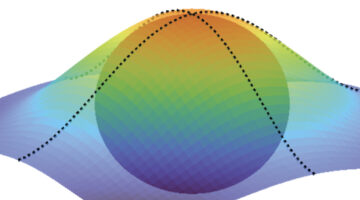
Mapping the Quantum Landscape of Electrons in Solids
Researchers found a way to reconstruct quantum geometric tensors (QGTs)—mathematical entities that encode how an electron’s wave function is shaped by its quantum environment. The mapping of QGTs enables the discovery and control of novel quantum phenomena such as superconductivity and unconventional electronic phases. Read more »![]()
![]()
Bennu’s Ancient Brine Sheds Light on Recipe for Life
Researchers traced the evolution of minerals (“salts”) in an ancient brine, as recorded in samples from the asteroid Bennu, returned to Earth by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission. The results support the idea that asteroids like Bennu may have delivered water and essential chemical building blocks of life to Earth in the distant past. Read more »![]()
![]()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 13
- Next Page »