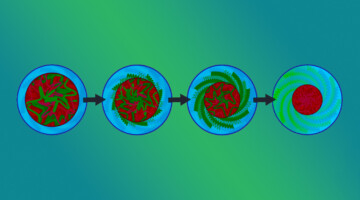
Adding “bulky” organic molecules earlier in solar-film synthesis slows crystal growth, leading to the formation of a protective surface layer that improves durability and efficiency. These next-gen materials could revolutionize solar-cell technology, offering increased efficiency, lower cost, lighter weight, and flexible solar modules. Read more »![]()
![]()
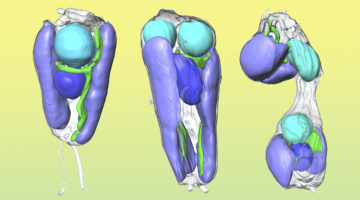
Symbiotic Nitrogen-Fixing Microbe Evolves into Organelle
Researchers found that a symbiont capable of fixing nitrogen (turning it into a biologically usable form) has evolved into an organelle—an intrinsic part of the algae cells that host it. The discovery is of great interest for understanding organelle genesis and for efforts to engineer agricultural plants with built-in nitrogen-fixing capabilities. Read more »![]()
![]()
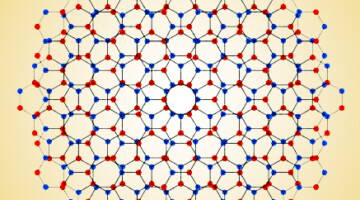
Big Twist Leads to Tunable Energy Gaps in a Bilayer Stack
Researchers found that twisting 2D layers at atypically large angles opens up potentially useful energy gaps in the material’s band structure. The results suggest a new way to tune materials for optoelectronic applications and provide a platform for exploring novel “moiré” phenomena beyond those observed at small twist angles. Read more »![]()
![]()
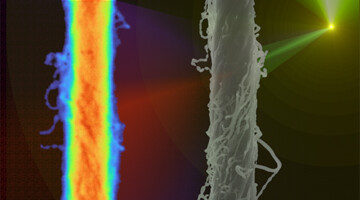
Tracking the Breakdown of Cellulose at the Micron Scale
A time-resolved study using infrared spectromicroscopy in a carefully controlled environment revealed why enzymes get bogged down when trying to break up cellulose from plants. The work sheds new light on the challenge of extracting the sugars locked up in plants for use in making petroleum-free fuels, chemicals, and medicines. Read more »![]()
![]()
How Processing Affects Structure in Composite Nanotube Yarns
Using the ALS, researchers found quantitative correlations between processing parameters and the structure of ultrafine, polymer-reinforced carbon-nanotube fibers. The work will facilitate the production of high-strength materials, including those needed for positioning target capsules for fusion research at the National Ignition Facility. Read more »![]()
![]()
Flat Bands Signal Electrons Trapped in 3D
Researchers found flat electronic band structures—known hallmarks of electrons trapped in two dimensions—but in a material that extends this phenomenon to three dimensions. The work opens up a material framework for exploring superconductivity and other exotic states in three dimensions for advanced electronic applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
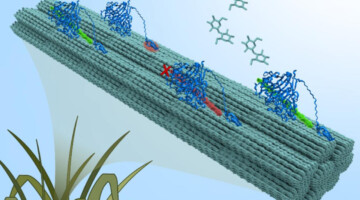
Computer-Aided Protein Design for New Biomaterials
Using a computer-based approach, researchers designed porous protein crystals that were revealed to be stable, tunable, and atomically accurate using x-ray scattering and diffraction at the ALS. The work provides a powerful new platform for biological materials engineering and opens up wide applications in biotechnology and medicine. Read more »![]()
![]()
Internal Currents in Lithium Batteries after Fast Charging
In lithium batteries after fast charging, researchers measured the persistence of internal currents and found that large local currents continue even after charging has stopped. The work uses hard x-ray 3D imaging in a novel way and sheds light on the causes of thermal runaway and the catastrophic failure of lithium batteries at rest. Read more »![]()
![]()
Insight into How Thermoresponsive Nanomaterials Work
By combining soft x-ray scattering with electron microscopy, researchers learned how nanoscale polymer assemblies in solution restructure in response to heating. The approach can be generalized to many complex, solution-phase, nanoscale processes, and holds promise for driving advances in applications from drug delivery to catalysis. Read more »![]()
![]()
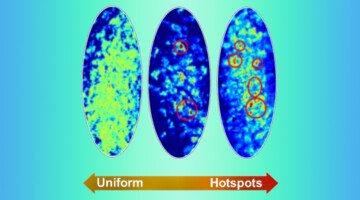
Fluctuations Mark Phase Changes in Magnetic Films
Researchers discovered that nanoscale spin fluctuations deep inside ordered states of a magnetic film can characterize phase transitions, independent of underlying magnetic interactions. The results provide a new way to predict and understand phase transitions in materials relevant to high-density, energy-efficient microelectronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- …
- 13
- Next Page »