Field-driven transport systems offer the possibility of biofunctionalized carriers for microrobotics, biomedicine, and cell delivery. Here, researchers show how magnetic fields may selectively manipulate and drive microrobotics along a patterned micromagnet. Different-sized magnetic carriers move in multiple directions, including selective rotation and bidirectional movement. Such steering systems can direct the delivery of drugs or cells into artificial microvascular channels. Read more »
ALS Work Using Microscopy/Imaging
These techniques use the light-source beam to obtain pictures with fine spatial resolution of the samples under study and are used in diverse research areas such as cell biology, lithography, infrared microscopy, radiology, and x-ray tomography.
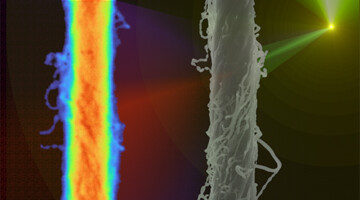
How Processing Affects Structure in Composite Nanotube Yarns
Using the ALS, researchers found quantitative correlations between processing parameters and the structure of ultrafine, polymer-reinforced carbon-nanotube fibers. The work will facilitate the production of high-strength materials, including those needed for positioning target capsules for fusion research at the National Ignition Facility. Read more »![]()
![]()
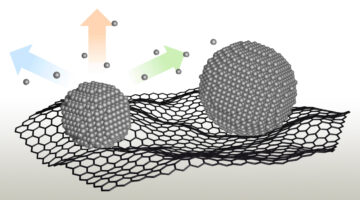
Tracking Platinum Movement on Fuel-Cell Electrodes
Researchers tracked the movement of the platinum nanoparticles that catalyze reactions in polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs) and correlated this movement with nanoparticle degradation. The results yielded solutions that can immediately reduce platinum waste in emission-free heavy-duty fuel-cell vehicles. Read more »![]()
![]()
“Computer Vision” Review of X-Ray Movies Leads to New Insights
Using a type of machine learning called “computer vision” to mine data from x-ray movies, researchers made new discoveries about the reactivity of a material in rechargeable batteries. The results suggest that optimizing the carbon layer thickness on the electrode surface could help researchers to design more efficient batteries. Read more »
Why Do Batteries Sometimes Catch Fire and Explode?
In order to better understand how a resting battery might undergo thermal runaway after fast charging, scientists are using a technique called “operando x-ray microtomography” to measure changes in the state of charge at the particle level inside a lithium-ion battery after it’s been charged. Read more »
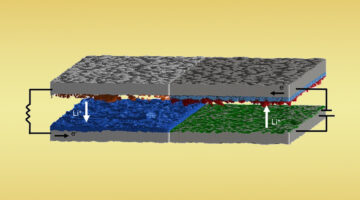
Internal Currents in Lithium Batteries after Fast Charging
In lithium batteries after fast charging, researchers measured the persistence of internal currents and found that large local currents continue even after charging has stopped. The work uses hard x-ray 3D imaging in a novel way and sheds light on the causes of thermal runaway and the catastrophic failure of lithium batteries at rest. Read more »![]()
![]()
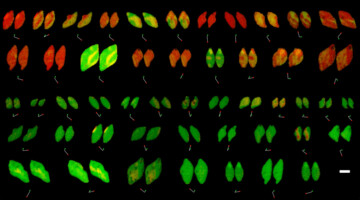
Improving Carbon Retention in Grassland Soil from Point Reyes
Soil organic carbon directly influences the life-supporting services provided by soils, including the production of food and the regulation of atmospheric carbon dioxide. To better understand how minerals such as calcium affect carbon accumulation in soil, researchers studied soils collected from Point Reyes National Seashore. Read more »![]()
HyMARC Aims to Hit Targets for Hydrogen Storage Using X-Ray Science
Understanding how materials absorb and release hydrogen is the focus of the Hydrogen Materials Advanced Research Consortium (HyMARC). At the ALS, the HyMARC Approved Program was recently renewed, underscoring the key role that soft x-ray techniques have played in addressing the challenges of hydrogen storage. Read more »
A Deep-Learning Analysis of Lithium-Plating Dynamics in Batteries
Lithium-metal solid-state batteries are a promising technology, but the deposition (plating) of lithium metal on electrode surfaces remains a significant technical hurdle. Here, researchers used micro-computed tomography data to train an artificial intelligence model to identify characteristics vital to improving battery performance. Read more »![]()
Will Chueh to Receive the 2023 Shirley Award
Will Chueh of Stanford University is the 2023 winner of the Shirley award for Outstanding Scientific Achievement at the ALS. His selection recognizes Chueh’s deep contributions in operando soft x-ray spectromicroscopy for imaging electrochemical redox phenomena—images and movies for battery and electrocatalytic reactions. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- …
- 19
- Next Page »