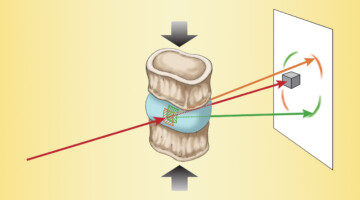
Researchers found that type 2 diabetes induces earlier onset of plastic (nonrecoverable) deformation in intervertebral discs by impairing the biomechanical behavior of collagen. A greater understanding of the underlying causes of tissue failure in diabetes—a growing problem worldwide—is important in helping to prevent and treat symptoms. Read more »![]()
ALS Work Using Scattering/Diffraction
These techniques make use of the patterns of light produced when x-rays are deflected by the closely spaced lattice of atoms in solids and are commonly used to determine the structures of crystals and large molecules such as proteins.
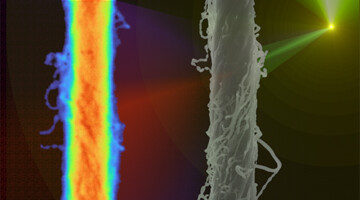
How Processing Affects Structure in Composite Nanotube Yarns
Using the ALS, researchers found quantitative correlations between processing parameters and the structure of ultrafine, polymer-reinforced carbon-nanotube fibers. The work will facilitate the production of high-strength materials, including those needed for positioning target capsules for fusion research at the National Ignition Facility. Read more »![]()
![]()
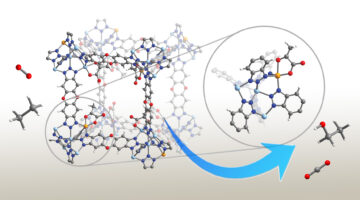
A Bio-Inspired Metal-Organic Framework for Capturing Wellhead Gases
Burning of natural gas at oil and gas wells, called flaring, is a major waste of fossil fuels and a contributor to climate change. In this work, researchers synthesized and characterized a metal-organic framework that uses biomimetic chemistry to convert wellhead gases into economically valuable feedstocks for petrochemical products. Read more »
Correlating Conformational Equilibria with Catalysis in the Electron Bifurcating EtfABCX of Thermotoga maritima
Anaerobic SEC-MALS-SAXS at the SIBYLS beamline probes the conformational states behind electron bifurcation in the Thermotoga maritima EtfABCX, revealing insights on mechanisms at the thermodynamic limits of life. Shown are the bifurcation- and electron-conducting-like states experimentally observed for the first time in solution. Read more »
Tracking Platinum Movement on Fuel-Cell Electrodes
Researchers tracked the movement of the platinum nanoparticles that catalyze reactions in polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs) and correlated this movement with nanoparticle degradation. The results yielded solutions that can immediately reduce platinum waste in emission-free heavy-duty fuel-cell vehicles. Read more »![]()
![]()
Computer-Aided Protein Design for New Biomaterials
Using a computer-based approach, researchers designed porous protein crystals that were revealed to be stable, tunable, and atomically accurate using x-ray scattering and diffraction at the ALS. The work provides a powerful new platform for biological materials engineering and opens up wide applications in biotechnology and medicine. Read more »![]()
![]()
Influences of Metal Electrodes on Stability of Non-Fullerene Acceptor-Based Organic Photovoltaics
Researchers investigate interfaces in an organic photovoltaic device, revealing that the aluminum (Al) top electrode undergoes thermally activated diffusion into inner layers forming ionic and organo-metallic-like species, compromising long-term device performance. Chemical degradation process is characterized by 27Al solid-state NMR and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Read more »
Immune Response Spurs Growth of “Soft” Kidney Stones
Matrix stones are an unusual type of soft kidney stone closely associated with the presence of bacteria from unchecked urinary tract infections. Researchers conducted a comprehensive study of surgically extracted matrix stones, work that highlights how host defense mechanisms against microbes can simultaneously encourage harmful stone formation. Read more »
How Structure Affects the Activity of Lipid Nanoparticles
Berkeley Lab and Genentech scientists related the internal structures of lipid nanoparticles to their efficacy at drug delivery, using a combination of methods including x-ray scattering at the ALS. The work promises to expedite the development of drug delivery systems for the treatment of diseases such as COVID-19 and cancer. Read more »![]()
![]()
Accelerating Sustainable Semiconductors With ‘Multielement Ink’
Scientists have developed “multielement ink”—the first “high-entropy” semiconductor that can be processed at low temperature or room temperature. The new semiconducting material could accelerate the sustainable production of next-gen microelectronics, photovoltaics, solid state lighting, and display devices. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- …
- 39
- Next Page »