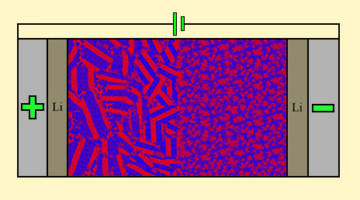
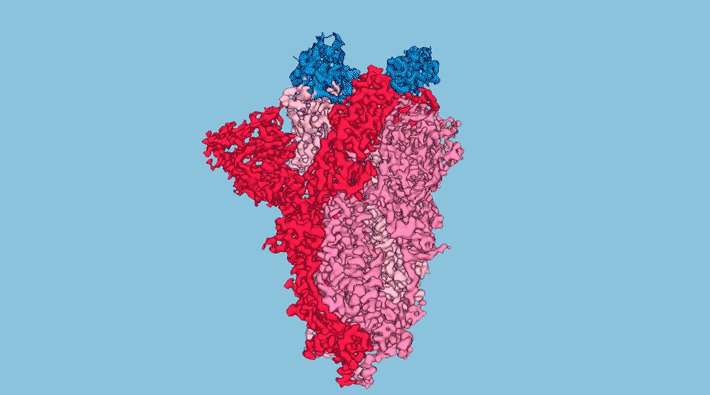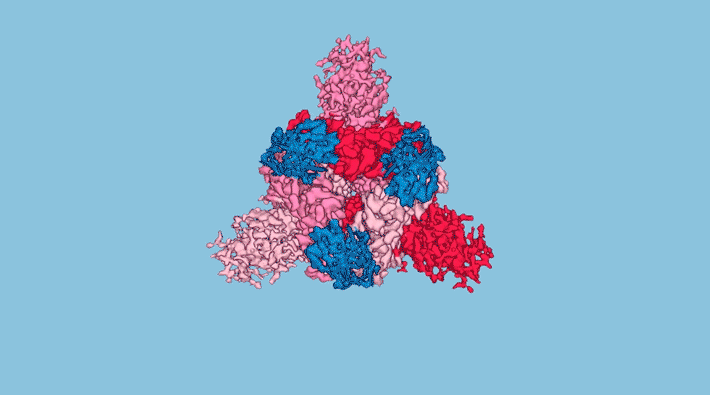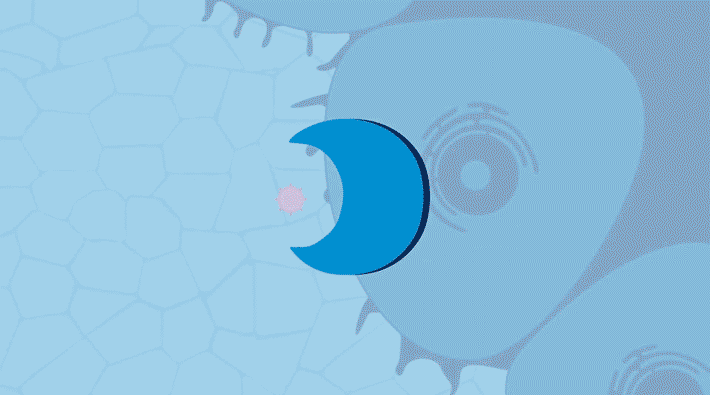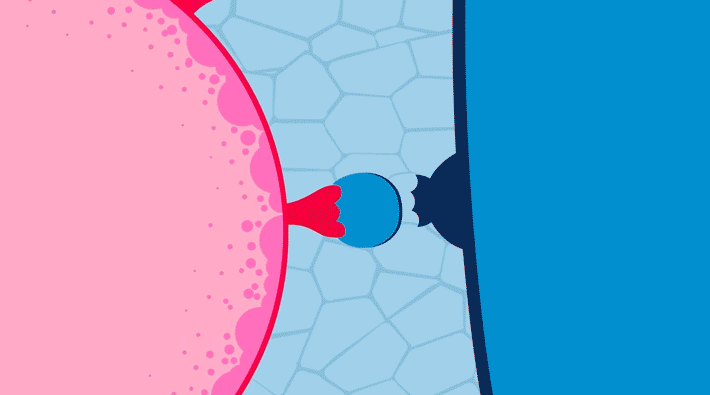
Researchers found that when an ion-conducting polymer composite is placed in an electric field, it forms ion-rich hotspots that continue to grow for hours after the field is removed. The study opens a new path to understanding the dynamic structure of composite materials for smaller, lighter batteries. Read more »![]()
![]()
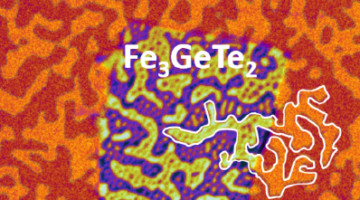
2D MXene Shows Evidence of a Magnetic Transition
A variety of experiments, including ALS x-ray studies, provided direct evidence of a magnetic transition in a 2D compound called a MXene (pronounced “maxene”). The finding adds new functionality to a family of materials with numerous ways to fine-tune properties for applications ranging from spintronic devices to electromagnetic shielding. Read more »![]()
![]()
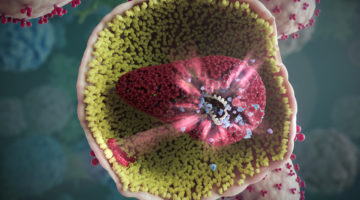
Inhalable COVID-19 Protection via Synthetic Nanobodies
Protein structures obtained in part at the ALS helped researchers to increase the potency of simplified antibodies (nanobodies) designed to neutralize SARS-CoV-2. Stable enough to be used in inhalers or nasal sprays, the nanobodies offer a new option, aside from injected vaccines, for COVID-19 prevention and treatment. Read more »![]()
![]()
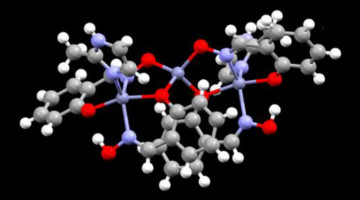
Molecular Complex Removes Copper Ions from Water
X-ray analyses provided key insights into the copper uptake mechanisms in a new organic-inorganic hybrid material that quickly and selectively removes copper ions from water. The material provides an efficient tool for copper remediation as well as a blueprint for creating other hybrid materials for removing toxic metals from water. Read more »![]()
![]()
From Stripes to Skyrmions in a Surprising Material
Researchers showed that tiny bubbles of ordered spins (skyrmions) can be induced to form in a material previously considered incompatible with skyrmion formation. The discovery opens up a new class of material systems that exhibit technologically desirable nanoscale features attractive for spintronic applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Super-Resolution Measurement of X-Ray Mirrors
ALS researchers, in collaboration with software and nanofabrication small businesses, developed a way to improve the accuracy of instruments that measure the surfaces of x-ray mirrors. The work significantly improves the quality of the data needed for the fabrication and optimal performance of advanced x-ray beamlines and space telescopes. Read more »![]()
![]()
Microstructures Explain Beetle Exoskeleton Strength
Using microtomography and other techniques, researchers identified the exoskeletal toughening mechanisms that explain the crush resistance of the aptly named diabolical ironclad beetle. The observations could be applied in developing tough, impact- and crush-resistant materials for joining dissimilar materials. Read more »![]()
![]()
Experimental Drug Targets HIV in a Novel Way
Researchers from Gilead Sciences Inc. solved the structure of an experimental HIV drug bound to a novel target: the capsid protein that forms a shield around the viral RNA. The work could lead to a long-lasting HIV treatment that overcomes the problem of drug resistance and avoids the need for burdensome daily pill-taking. Read more »![]()
![]()
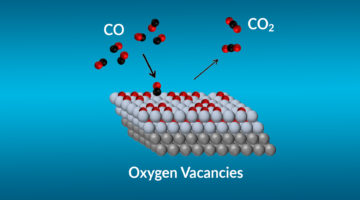
Increasing the Efficiency of CO Catalytic Conversion
Using a combination of tools at the ALS and other facilities, researchers probed specific mechanisms affecting the efficiency of catalysts for CO-to-CO2 conversion. The work brings us closer to the rational design of more effective catalysts for cleaning up toxic CO exhaust and advances our understanding of fundamental catalytic reactions. Read more »![]()
![]()
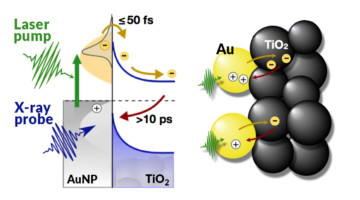
A Probe of Light-Harvesting Efficiency at the Nanoscale
Using time-resolved experiments at the ALS, researchers found a way to count electrons moving back and forth across a model interface for photoelectrochemical cells. The findings provide real-time, nanoscale insight into the efficiency of nanomaterial catalysts that help turn sunlight and water into fuel through artificial photosynthesis. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- …
- 13
- Next Page »